2개월 간격 애플리버셉트 주사에 제한적 반응인 습성 나이관련황반변성에서 주사 간격 단축의 효과
Efficacy of Injection Interval Shortening in Neovascular Age-related Macular Degeneration with Limited Response to Bimonthly Aflibercept
Article information
Abstract
목적
2개월 간격 애플리버셉트 주사에 반응이 제한적인 습성 나이관련황반변성 환자에서 2개월 미만으로 주사 간격을 단축하여 시행한 결과를 보고하고자 한다.
대상과 방법
2개월 간격 애플리버셉트 주사에도 불구하고 망막하액 혹은 망막내액이 완전히 소실되지 않는 습성 나이관련황반변성에서 2개월 이내 간격 애플리버셉트 주사(단축 주사)를 시행받은 환자를 대상으로 후향적 의무기록 분석을 시행하였다. 단축 주사 직전의 시력과 중심망막두께를 단축 주사 후의 값과 서로 비교하였으며, 망막부종이 완전히 소실되는 비율을 추가적으로 확인하였다.
결과
전체 28명을 대상으로 연구를 시행하였다. 진단 시부터 단축 주사 전까지의 기간은 평균 43.0 ± 20.5개월이었으며, 최초 단축 주사 간격은 8안에서 5주, 20안에서 6주였다. 최대교정시력은 단축 주사 전 평균 logarithm of minimal angle of resolution 0.37 ± 0.21에서 1회 단축 주사 후 평균 0.32 ± 0.20으로 변화하였으며(p=0.075). 중심망막두께의 경우 평균 389.3 ± 73.7 m에서 단축 주사 후 평균 242.1 ± 91.9 m로 유의하게 감소하였다(p<0.001). 11안(39.3%)에서 1회 단축 주사 후 망막부종이 완전히 소실되었으며, 15안(53.6%)에서 2회 이상의 주사 후 부종이 소실되었다.
결론
2개월 간격 애플리버셉트 주사에 반응이 제한적인 습성 나이관련황반변성에서 2개월 이내 간격의 단축 주사는 비교적 좋은 해부학적 효과를 보였으나 시력 개선 효과는 제한적이었다. 향후 장기 결과에 대한 평가가 필요할 것이다.
Trans Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the effectiveness of shortening the injection interval to < 2 months in neovascular age-related macular degeneration (AMD) with limited response to bimonthly aflibercept injections.
Methods
We performed a retrospective analysis of medical records for neovascular AMD patients who received aflibercept injections with < 2 month intervals (shortened injection) because of limited response to bimonthly injections. The best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) and central retinal thickness (CRT) were compared before and after shortened injections. The incidence of complete resolution of retinal edema was also analyzed.
Results
A total of 28 patients were included, with a mean duration between diagnosis and shortened injection of 43.0 ± 20.5 months. The interval of the first shortened injection was 5 weeks in 8 eyes and 6 weeks in 20 eyes. BCVA changed from mean logarithm of minimal angle of resolution of 0.37 ± 0.21 to 0.32 ± 0.20 after shortening (p = 0.075). The mean CRT reduced significantly from 389.3 ± 73.7 μm to 242.1 ± 91.9 μm after shortening (p < 0.001). Retinal fluids resolved completely in 11 (39.3%) eyes after a single shortened injection, and in 15 (53.6%) eyes after two or more shortened injections.
Conclusions
Shortening the injection interval to < 2 months had good anatomical efficacy in neovascular AMD with limited response to bimonthly aflibercept injections. However, the efficacy for improvement in visual acuity was limited. Further studies are required to investigate the long-term outcomes.
애플리버셉트(aflibercept)는 습성 나이관련황반변성의 치료에 효과적인 항혈관내피성장인자 약제로1 현재 국내 여러 병원에서 널리 이용되고 있다.2 애플리버셉트는 다른 항혈관내피성장인자 약제인 라니비주맙에 비해 지속 시간이 더 긴 것으로 알려져 있는데,3 초기 임상 시험에서 8주 간격 애플리버셉트 주사가 4주 간격 라니비주맙 주사에 비해 열등하지 않은 치료 결과를 보였다.1
애플리버셉트가 습성 나이관련황반변성의 치료를 위해 2014년 국내에 처음 도입되었을 때 최소 주사 간격 2개월로 허가를 받게 되었다. 그러나 이러한 국내 허가 사항은 애플리버셉트 치료에 있어서 2개월 미만 주사가 필요할 수 있음을 명시한 해외 consensus4-7를 완전히 반영하지 못한다는 제한점이 있었다.
비교적 최근인 2021년 7월부터는 시력 혹은 해부학적 검사 결과가 악화되는 경우 최소 4주 간격까지 애플리버셉트 주사를 시행할 수 있도록 국내 허가 사항이 변경되어 이러한 제한점이 해소되었다. 과거 Mitchell et al8의 연구에서 8주 간격의 주사에 효과가 충분하지 않은 경우 주사를 최소 4주까지 단축시켜 치료한 바 있으며, Muftuoglu et al9의 연구에서는 8주 간격의 애플리버셉트 주사에 효과가 제한적인 경우를 대상으로 4주 간격 애플리버셉트 주사를 시행한 결과를 보고한 바 있다. 그러나 이러한 방식의 효과에 초점을 맞춘 연구 결과는 아직 소수만이 발표되어 있으며, 더 나아가 현재까지 국내 환자를 대상으로 2개월 이내 간격 애플리버셉트 주사의 효과를 평가한 연구 결과는 발표된 바 없다.
애플리버셉트는 고가의 약제이며, 따라서 가능한 효율적인 약제의 이용이 필요하다. 환자를 치료하는 의사가 환자에게 알맞은 효과적이면서 효율적인 주사 간격을 결정하는 데 있어서 다양한 간격으로 주사를 시행한 연구들이 유용한 정보를 제공할 수 있으나, 현재 이와 같은 자료가 충분하지 않은 실정이다. 이에 본 연구에서는 2개월 간격 애플리버셉트 주사에 반응이 제한적인 습성 나이관련황반변성 환자에서 2개월 미만으로 주사 간격을 단축하여 시행한 결과를 보고하고자 한다.
대상과 방법
본 후향적 연구는 단일기관에서 헬싱키선언에 입각하여 시행되었으며, Institutional Review Board (IRB) 승인을 획득하였다(Kim's Eye Hospital IRB, #2023-01-003). 습성 나이관련황반변성으로 진단되어 치료를 시행받던 중 2개월 간격의 애플리버셉트 주사에 반응이 제한적인 것으로 판명되어 2022년 5월부터 2022년 10월 사이에 단일 의사(J.H.K.)에 의해 2개월 미만 간격의 애플리버셉트 주사를 시행받은 환자를 대상으로 연구를 시행하였다. 이전에 유리체망막수술을 시행받은 병력이 있는 경우 연구에서 제외하였다.
연구에 포함된 환자들은 진단 시 안저검사와 빛간섭단층촬영, 형광안저혈관조영검사, 인도사이아닌그린혈관조영술 검사를 시행받았다. 혈관신생의 종류는 인도사이아닌그린 혈관조영술 결과를 바탕으로 분류하였는데, 분지혈관망과 결절 모양 과형광 병변이 발견되는 경우 결절맥락막혈관병증으로 분류하였으며,10 이러한 소견이 관찰되지 않는 경우에는 전형적 습성 나이관련황반변성으로 분류하였다.
모든 환자들은 습성 나이관련황반변성 진단 직후 1개월 간격 3회 애플리버셉트 혹은 라니비주맙 주사를 시행받은 후 의사의 판단에 따라 재발할 때에만 주사를 시행하는 as-needed 방식11 혹은 재발 여부와 관계없이 지속적으로 주사하는 treat-and-extend 방식12을 이용하여 치료를 시행받았다. 진단 직후 라니비주맙 주사를 시행받은 환자들 중 추적 관찰 기간 동안 라니비주맙에 효과가 제한적인 것으로 판단된 경우 애플리버셉트로의 교체투여를 시행하였다. 모든 치료는 한 명의 숙련된 전문의가 시행하였다.
치료 중 2개월 간격으로 최소 2회 이상 애플리버셉트 주사 후 2개월 시점에 검진하였을 때, 망막내액, 망막하액, 혹은 망막하고반사병변(subretinal hyperreflective material)이 지속되는 경우 치료에 대한 반응이 제한적인 것으로 판단하였으며, 애플리버셉트 주사 간격을 2개월 미만으로 단축하였다. 기존의 treat-and-extend 방식에서 치료 효과가 충분하지 않은 경우 2주 간격으로 주사 간격을 단축하는 방식을 이용하고 있으므로12 최소 2주 이상 주사 간격을 단축한다면 어느 정도 효과가 있을 것으로 추측하고 단축 주사는 6주 이내 간격으로 시행하는 것을 원칙으로 하였다. 이후 환자와의 상의를 통해 구체적인 주사 간격을 결정하였는데, 효율적인 치료를 위해 한 번에 4주까지 주사 간격을 단축하지 않고 5주 혹은 6주 간격까지 단축하는 방식을 주로 이용하였다. 주사 간격 단축의 필요성에 대해 환자와 충분히 상의하였으며, 환자의 병원 방문 가능 일정 등을 전반적으로 고려하여 주사 간격을 최종 결정하였다. 주사 간격을 7주 간격까지 소폭 단축하는 것은 뚜렷한 효과가 없을것으로 판단되어 본 연구에서는 시행되지 않았다. 주사 간격 단축 후 망막내액/망막하액/망막하고반사병변이 완전히 소실된 환자 중 일부에서는 의사의 판단에 따라 환자와 충분히 상의 후 주사 간격을 2개월로 다시 연장하였다.
결과 분석을 위해 다음과 같은 정보를 수집하였다: 나이, 성별, 혈관신생의 종류, 이전에 라니비주맙 주사 병력, 진단 시부터 2개월 이내 주사(단축 주사) 시작 시점까지의 기간과 이전에 시행된 항혈관내피성장인자 주사 횟수, 단축 주사 시점의 최대교정시력과 중심망막두께 및 빛간섭단층촬영 상의 망막내액/망막하액/망막하고반사병변/장액성 망막색소상피박리 유무, 첫 단축 주사의 주사 간격 및 주사 후 최대교정시력, 중심망막두께 및 빛간섭단층촬영 상의 망막내액/망막하액/망막하고반사병변/장액성 망막색소상피박리 유무, 총 단축 주사 횟수 및 주사 간격, 단축 주사를 모두 시행한 후 빛간섭단층촬영상 망막내액/망막하액/망막하고 반사병변 완전 소실 유무, 다시 주사 간격을 2개월로 연장한 환자들의 경우 주사 후 2개월 시점의 빛간섭단층촬영상 망막내액/망막하액/망막하고반사병변 재발 유무를 추가적으로 확인하였다.
단축 주사 시점에 측정된 최대교정시력과 중심망막두께를 첫 단축 주사 후 측정된 값과 서로 비교하였으며, 망막내액/망막하액/망막하고반사병변/장액성 망막색소상피박리가 관찰되는 비율 역시 서로 비교하였다. 망막내액/망막하액/망막하고반사병변이 완전히 소실된 것을 망막부종의 완전한 소실로 정의하였으며, 단축 주사 후 망막부종의 환전한 소실 여부를 평가하였다. 또한 단축 주사 후 logarithm of minimal angle or resolution (logMAR) 시력이 0.2 이상 호전되거나 중심망막두께가 300 μm 이하로 감소한 비율을 추가적으로 확인하였다. 주사 간격을 다시 2개월로 연장한 환자들의 경우 2개월 시점에 망막내액/망막하액/망막하고 반사병변의 재발 여부를 확인하였다.
추가적으로 전형적 습성 나이관련황반변성과 결절맥락막혈관병증 사이에 첫 단축 주사 후 최대교정시력과 중심망막두께의 변화량을 서로 비교하였다.
통계 분석에는 SPSS 프로그램(SPSS ver. 12.0 for Windows, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA)을 이용하였다. 시력은 logMAR 값을 이용하여 분석하였다. 서로 다른 두 시점 사이의 비교에는 Wilcoxon signed-ranks test를 이용하였으며, 서로 다른 두 군 사이의 비교에는 Mann-Whitney U test를 이용하였다. 0.05 미만의 p값을 통계적으로 유의한 값으로 정의하였다.
결 과
전체 28안(28명)을 대상으로 연구를 시행하였으며, 환자의 평균 연령은 72.4 ± 7.9세였다(Table 1). 혈관신생의 종류는 전형적 습성나이관련황반변성이 14안(50.0%), 결절맥락막혈관병증이 14안(50.0%)이었다. 5안의 경우 최초 진단 후에는 라니비주맙으로 투여하다 도중에 애플리버셉트로 교체하였던 경우였으며 나머지 23안은 최초 진단 시부터 애플리버셉트만을 이용하여 치료한 경우였다.
진단 시부터 단축 주사 전까지의 기간은 평균 43.0 ± 20.5개월이었으며, 상기 기간 동안 평균 16.9 ± 7.3회의 항혈관 내피성장인자 주사가 시행되었다. 단축 주사 직전까지 평균 5.2 ± 2.7회의 연속적인 2개월 간격 애플리버셉트 주사가 시행되었는데, 주사 간격은 최소 56일, 최대 64일이었으며, 평균 58.0 ± 1.2일이었다. 최초 단축 주사 간격은 8안(28.6%)에서 5주, 20안(71.4%)에서 6주였는데, 전체 환자에서 총 81회의 주사가 시행되어 평균 주사 횟수는 2.8 ± 1.3회였으며, 평균 주사 간격은 5.7 ± 0.6주였다. 24안에서 2회 이상의 연속적인 단축 주사가 시행되었는데, 1안에서만 주사 간격을 4주까지 단축하였다.
최초 단축 주사 전 측정된 logMAR 최대교정시력은 0.37 ± 0.21이었으며, 1회 단축 주사 후 0.32 ± 0.20으로 변화하였다(Fig. 1A) (p=0.072). LogMAR 0.2 이상의 시력 호전은 2안(7.1%), 0.1 이상 0.2 미만의 시력 호전은 5안(17.9%)에서 나타났으며, 나머지 21안(75.0%)의 경우 단축 주사 전후로 시력의 뚜렷한 변화가 없었다. 중심망막두께의 경우 단축 주사 전 389.3 ± 73.7 μm였으며, 단축 주사 후 242.1 ± 91.9 μm로 유의하게 감소하였다(Fig. 1B) (p<0.001). 중심망막 두께가 300 μm 이상이었던 경우는 단축 주사 전 23안(82.1%)이었으며, 단축 주사 후 13안(46.4%)이었다.

Changes in best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) (A) and central retinal thickness (B) in patients who underwent shortening of aflibercept injections. (A) When compared to the BCVA before the shortening, the BCVA slightly improved after the shortening. However, there was no statistical difference between the two time points. (B) When compared to the central retinal thickness before the shortening, the thickness significantly decreased after the shortening. LogMAR = logarithm of minimal angle of resolution.
전형적 습성 나이관련황반변성과 결절맥락막혈관병증 사이의 비교에서 시력의 변화량(0.06 ± 0.08 vs. 0.03 ± 0.06, p=0.401)과 중심망막두께의 변화량(71.4 ± 56.8 μm vs. 58.9 ± 59.1 μm, p=0.511) 사이에는 유의한 차이가 없었다.
단축 주사 전 빛간섭단층촬영에서 망막하액, 망막내액, 망막하고반사병변 및 장액성 망막색소상피박리가 관찰된 비율은 각각 100.0% (28안), 3.6% (1안), 46.4% (13안) 및 75.0% (21안)였으며, 1회 단축 주사 후 각각 60.7% (17안), 0%, 3.6% (1안) 및 46.4% (13안)으로 변화하였다(Fig. 2). 11안(39.3%)의 경우 1회 단축 주사만으로 망막부종이 완전히 소실되는 결과를 보였으며(Fig. 3, 4), 4안의 경우 2회 이상의 단축 주사 후 망막부종이 소실되었다(Fig. 5). 최종적으로 망막부종이 완전히 소실된 15안 중 5안에서 주사 간격을 다시 2개월로 연장하였는데, 3안(60%)에서는 주사 후 2개월 시점에도 망막부종이 재발하지 않았으나(Fig. 3) 나머지 2안(40%)에서는 부종이 재발하는 결과를 보였다(Fig. 4).
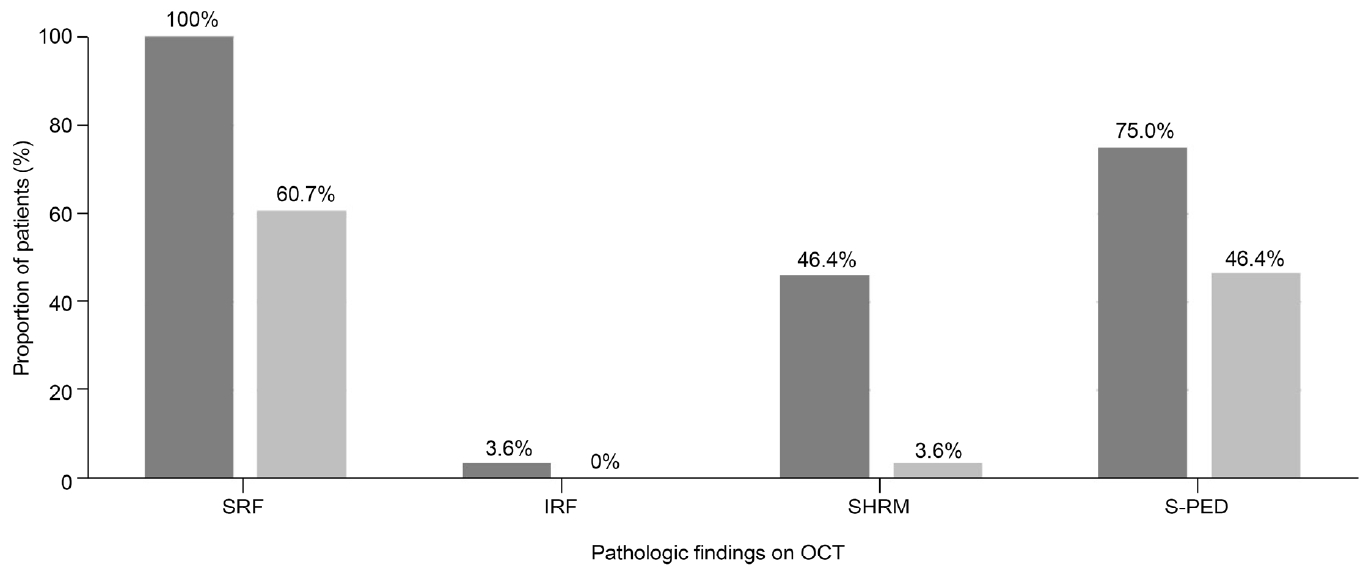
Bar graphs showing proportion of patients with subretinal fluid (SRF), intraretinal fluid (IRF), subretinal hyperreflective material (SHRM), and serous pigment epithelial detachment (S-PED) before (dark gery bars) and after (light grey bars) shortening of injection interval. Note that the proportion of all four pathologic findings on optical coherence tomography (OCT) decreased after the shortening of injection interval.

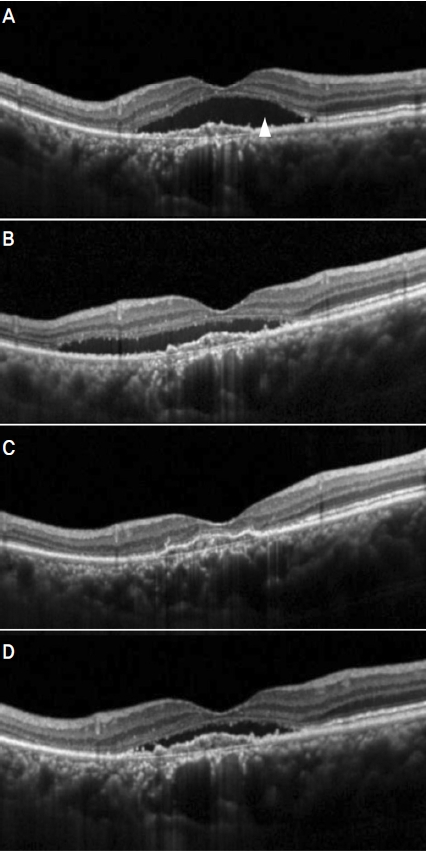
A representative case showing clinical course of a 65-year old patient who underwent shortening of injection interval. At 14 months after initial diagnosis (A), subretinal fluid (SRF) was noted. The SRF was not resolved during 9 consecutive bimonthly aflibercept injections (B). The patient underwent shortening of injection interval. After the 2 shortened injections with 5 and 6 week interval (C), all the retinal fluids were completely resolved. The retina maintained dry after the elongation of injection interval to 2 months (D).
A representative case showing clinical course of a 72-year old patient who underwent shortening of injection interval. At 56 months after initial diagnosis (A), subretinal fluid (SRF) was noted (arrowhead). The SRF was not resolved during 5 consecutive bimonthly aflibercept injections (B). The patient underwent shortening of injection interval. Six weeks after the first shortened injection (C), all the retinal fluids were completely resolved. However, recurrence of SRF was noted after the elongation of the interval to 2 months (D).
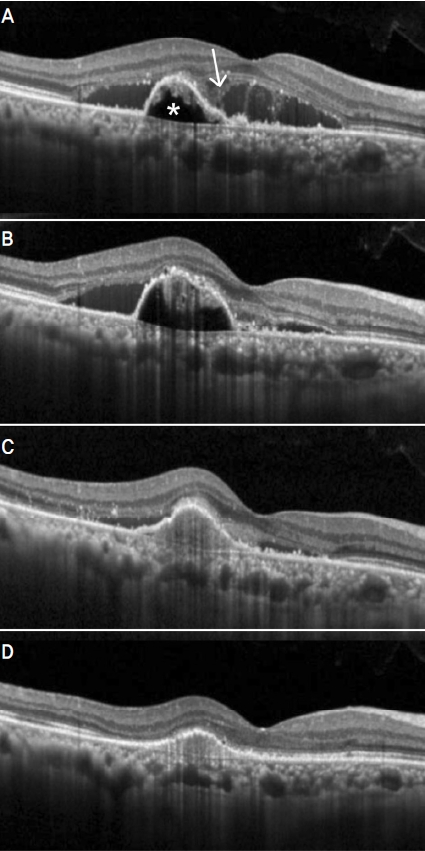
A representative case showing clinical course of a 62-year old patient who underwent shortening of injection interval. At 26 months after initial diagnosis (A), subretinal fluid (SRF) (arrowhead), subretinal hyper-reflective material (arrow), and serous pigment epithelial detachment (asterisk) was noted. The retinal edema was not resolved during 5 consecutive bimonthly aflibercept injections (B). The patient underwent shortening of injection interval. Six weeks after the first shortened injection (C), decreased retinal fluids were noted. The retinal fluid was completely resolved after 2 additional injections with 6 weeks interval (D).
고 찰
애플리버셉트의 효과 지속 시간을 평가한 기존 연구에 따르면 전방 내 혈관내피성장인자 A를 억제하는 기간은 평균 67일인 것으로 나타났다.3 그러나 효과 지속 시간이 2개월 미만인 경우도 있었으며 효과 지속 기간이 50% 이상 경과한 후에는 임상적으로 망막부종의 재발이 나타날 수 있는 것으로 보고되었는데,3 이와 같은 결과는 일부 환자들에서 2개월 간격 주사 효과가 임상적으로 충분하지 않을 수 있다는 점을 시사한다.
애플리버셉트를 이용 treat-and-extend 방식을 통해 습성나이관련황반변성을 치료한 기존 연구 결과들에서는 적지않은 수의 환자에서 8주 이내로 짧은 간격의 주사 치료가 필요한 것으로 나타났다. 애플리버셉트만을 이용하여 연구를 시행한 DeCroos et al13의 연구에서는 29%에서 8주 이내 간격의 주사가 필요하였으며, 라니비주맙과 애플리버셉트 치료 결과를 서로 비교한 Gillies et al14의 연구에서는 46%에서 8주 이내 간격의 주사가 필요하였다. 보다 최근 발표된 Mitchell et al8의 연구에서는 23%에서 치료 시작 후 평균 약 43주에 8주 이내 간격의 주사가 필요하였다.
애플리버셉트 약제를 도입하기 위한 임상 시험이었던 VEGF Trap-Eye: Investigation of Efficacy and Safety in Wet AMD(VIEW) study에서는 비록 8주 간격 주사군과 4주 간격 주사군 사이에 유의미한 결과 차이는 없었으나 중심망막두께 변화에 있어서 4주군이 안정적인 결과를 보인 데 반해 8주 군에서는 변동성이 나타났는데,1 이는 8주 간격 주사를 시행받은 환자 중 일부에서는 약제 효과의 감소와 함께 중심망막두께가 다시 두꺼워진 경우가 있었음을 시사한다.
VIEW study 결과를 보다 세부적으로 분석한 Jaffe et al15의 연구에서는 3회 loading 주사 후에도 망막부종이 완전히 소실되지 않은 환자들의 경우 지속적인 4주 간격의 주사가 치료 결과를 호전시키는 데에 도움이 된 것으로 나타났는데, 이는 특히 치료반응이 좋지 않은 환자들에서 주사 간격 단축의 필요성을 시사하는 결과라 할 수 있다. 실제로 결절맥락막혈관병증에서 애플리버셉트 단독 치료의 효과를 평가한 Aflibercept in Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy (PLANET) 연구에서는 8주 간격의 애플리버셉트 주사 중 제한적인 반응이 나타나는 경우 구조요법의 일환으로 주사 간격을 4주로 단축시키는 방법을 적용한 바 있다.16
실제로 8주 간격 애플리버셉트 주사에도 망막부종이 소실되지 않았던 39명의 환자를 대상으로 4주 간격 애플리버셉트 주사의 효과를 평가한 Muftuoglu et al9의 연구에서는 중심망막두께의 유의한 감소와 함께 약 50%에서 망막부종이 완전히 소실되는 결과를 보여 보다 짧은 간격 주사의 유용성을 확인하였다. 그러나 4주 간격 주사로 변경한 후에도 유의한 시력 호전은 나타나지 않아 기능적 부분에 있어서는 이러한 방법에 제한이 있다는 점 역시 확인할 수 있었다.
본 연구에서는 2회 이상의 2개월 간격 애플리버셉트 주사에도 망막부종이 완전히 소실되지 않은 환자를 대상으로 5-6주 간격의 애플리버셉트 주사를 시행하였는데, 1회 단축 주사 후 39.4%에서 완전한 부종의 소실이 나타났으며, 평균 5.7주 간격의 연속적인 단축 주사 후 최종적으로 53.6%에서는 부종이 완전히 소실되는 결과를 보였다. 이와 같은 결과는 4주 간격 주사를 통해 50%에서 망막부종의 완전한 소실을 얻었던 Muftuoglu et al9의 연구와 비슷한 결과였다.
현재까지 2개월 간격 애플리버셉트 주사에 반응이 제한적인 경우에서 어느 정도 간격으로 주사 간격을 단축시키는 것이 최선의 방법인가에 대해서는 아직 명확한 기준이 확립된 바 없다. 본 연구의 결과는 주사 간격을 단축할 때 한 번에 4주까지 단축하지 않고, 5-6주까지 약간만 단축하는 경우에도 상당수 환자에서 좋은 해부학적 결과를 얻을 수 있다는 점을 보여주고 있는데, 이는 보다 효율적인 애플리버셉트 치료를 계획하는 경우 참고할 수 있을 것으로 생각된다. 시력의 경우 일부 환자에서는 호전되는 경향이 있었으나 전체 환자에서 통계적으로 유의한 호전은 나타나지 않았는데, 4주 간격의 주사에서도 유의한 시력 호전이 없었던 Muftuoglu et al9의 연구 결과를 고려하였을 때, 본 연구에서 주사 간격을 4주로 단축하였다하더라도 뚜렷하게 더 나은 시력 결과를 얻기는 어려웠을 것으로 추측된다.
애플리버셉트 주사 치료는 재정적인 부분뿐 아니라 자주 병원을 방문하는 데에서 발생하는 시간적 부담,17 주사 자체에 대한 두려움과 통증18 등 다양한 방면에서 환자에게 큰 부담을 야기할 수 있다. 따라서 주사 간격을 2개월 이내로 단축하여 진행한 결과 망막의 부종이 완전히 소실되었다면 보다 효율적인 치료를 위해 다시 주사 간격을 2개월 이상으로 연장하는 방안을 고려해볼 수 있다.
Wolf et al19은 애플리버셉트를 이용하여 treat-and-extend 치료를 시행하던 중 8주 미만의 주사가 필요하였던 경우의 결과를 별도로 분석하였다. 상기 연구에서는 전체 환자의 23%에서 8주 미만의 주사가 필요하였는데, 이들 중 59.7%에서는 다시 주사 간격을 8주 이상으로 연장할 수 있었던 것으로 나타났다. 본 연구에서는 단축 주사 결과 망막부종이 완전히 소실되었던 15안 중 5안에서 주사 간격을 다시 2개월로 연장하였는데, 60%에서는 주사 간격 연장 후에도 망막부종이 재발하지 않아 Wolf et al19의 연구에서와 비슷한 비율을 보였다. 이와 같은 결과는 치료 과정에서 2개월 간격 애플리버셉트 주사에 반응이 충분하지 않아 주사 간격을 단축해야 하는 경우가 발생한다 해도 적지 않은 비율에서 다시 보다 효율적인 치료로 전환할 수 있다는 점을 시사한다.
애플리버셉트 2개월 간격 주사에 제한적 반응을 보이는 경우 일부 환자에서는 소량의 망막하액을 용인하며 주사를 지속하는 fluid-tolerating 방법을 적용해볼 수 있을 것이다. 비록 Guymer et al20의 임상 시험에서 이러한 방식을 이용한 치료 성적이 나쁘지 않았으나 분석 방식을 달리하였을 때, 망막하액의 잔존이 좋지 않은 시력과 연관될 수 있다는 점 역시 밝혀져21 fluid-tolerating 방식을 적용한 장기 치료에 있어서는 아직 주의가 필요한 상태이다. 다른 항혈관내 피성장인자 약제인 라니비주맙이나 브롤루시주맙으로의 교체투여 역시 고려해볼 만한 방법이다. 그러나 라니비주맙으로 교체투여의 경우 그 효과가 뚜렷하지 않은 경우가 많으며,22,23 브롤루시주맙의 경우 교체투여 후 해부학적 호전을 기대할 수 있는 반면 비교적 높은 안내염증 발생률을 감수해야 한다는 제한점이 있다.24 이와 같은 상황에서 애플리버셉트 약제를 그대로 이용하여 주사 간격을 단축시키는 방법은 실제 진료 환경에서 비교적 수월하게 이용할 수 있는 유용한 방안으로 생각된다.
과거 연구들에서 망막하액이 존재하는 경우에는 시력 혹 은 시력 예후와 큰 관련이 없거나 오히려 좋은 시력과의 연관성도 확인되었다.25 그러나 망막내액이 존재하는 경우에는 나쁜 시력 혹은 시력 예후와 밀접한 관련이 있는 것으로 보고되었다.25 이러한 결과를 고려하였을 때, 좋은 시력 결과를 위해서는 망막내액을 충분히 소실시켜야 할 수 있으며, 망막내액의 소실은 애플리버셉트 주사 간격 단축의 한 목표가 될 수 있을 것이다. 그러나 본 연구에서는 주사 간격 단축 전 망막내액이 관찰된 환자가 전체의 3.6%에 불과하여 단축 주사가 망막내액의 소실에 미치는 영향에 대해서는 명확하게 평가할 수 없었다. 이 부분에 대해서는 향후 망막내액이 관찰되는 다수의 환자를 대상으로 한 추가적인 연구가 필요할 것이다.
본 연구의 제한점은 다음과 같다. 본 연구는 후향적 연구로 비교적 적은 수의 환자를 대상으로 시행되었다. 단축주사의 적응증과 주사 간격에 대한 명확한 기준이 정립되어 있지 않았으며, 주사 간격을 2개월로 다시 연장하는 데에 대한 기준 역시 명확하지 않았다. 주로 5-6주 간격의 단축 주사를 시행하였으므로 본 연구의 결과는 4주 혹은 7주 간격의 단축 주사를 시행하는 경우를 반영하기 어려울 것이다. 마지막으로 단축 주사 전 망막내액이 관찰된 경우는 소수에 불과하였다.
요약하면 본 연구에서는 2개월 간격 애플리버셉트 주사에 반응이 제한적인 습성 나이관련황반변성 환자를 대상으로 2개월 미만 애플리버셉트 주사의 효과를 평가하였다. 5-6주 간격의 단축 주사 1회 시행 후 39.3%에서 망막부종이 완전히 흡수되었으며, 2회 이상의 단축 주사를 통해 53.6%에서 망막부종을 소실시킬 수 있었다. 또한 일부 환자에서는 다시 2개월 간격으로 주사 기간을 성공적으로 연장할 수 있었다. 2개월 미만 간격으로 애플리버셉트 주사 간격 단축을 고려할 때 본 연구의 결과를 참고할 수 있을 것이다. 향후 추가적인 연구를 통해 단축 주사 간격을 정할 때 참고할 수 있는 기준을 정립할 수 있다면 효율적이면서도 효과적인 치료에 더 크게 기여할 수 있을 것이다.
Notes
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
References
Biography
김민철 / Min Chul Kim
김안과병원
Kim’s Eye Hospital

