결절경화증의 표적치료제(Everolimus) 투여 후 호전된 망막성상세포과오종
Regressed Retinal Astrocytic Hamartomas in Tuberous Sclerosis by Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Inhibitor (Everolimus) Treatment
Article information
Abstract
목적
결절경화증 환아에서 mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) 억제제(everolimus) 치료 후 망막성상세포과오종 병변의 두께가 감소하는 호전을 보여 이를 보고하고자 한다.
증례요약
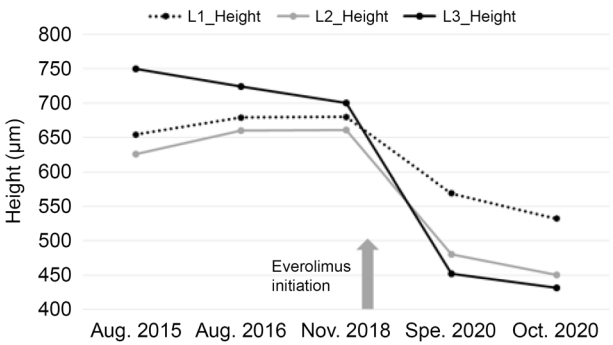
결절경화증으로 진단받은 12세 여아가 정기적 안저검사를 위해 방문하였다. 환아는 생후 3개월경 양안 안저에서 다발성성상세포과오종이 발견된 후 1년마다 경과 관찰하였고 만 10세경 안저검사까지 병변의 변화가 없었다. 마지막 검사 2개월 후 경련이 있어 치료를 위해 소아신경과에서 everolimus (5 mg, AFINITOR®, Novartis, Bazel, Switzerland)을 17개월간 처방하였고, 이후 시행한 안저검사와 빛간섭단층촬영에서 뚜렷한 3군데 과오종의 평균두께가 676 μm에서 500 μm로 25% 감소하였다.
결론
결절경화증 환자에서 mTOR 억제제는 심각한 부작용 없이 전신의 과오종과 경련을 치료할 수 있는 표적치료제이며, 일반적으로 자연적인 호전이 극히 드물다고 알려진 망막성상세포과오종의 크기를 감소시키는 효과가 있었다. 후극부나 시신경유두 주변에 발생하여 시력과 시야에 영향을 주는 과오종의 경우 everolimus를 치료적 수단으로 고려할 수 있겠다.
Trans Abstract
Purpose
We report a case of regressed retinal astrocytic hamartomas (RAHs) in tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) patients by mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor (everolimus) treatment.
Case summary
A 12-year-old girl diagnosed with TSC visited for regular checkups. The patient had undergone regular fundus examinations every year after the finding of multiple RAHs in both eyes in the initial screening at 3 months of age. There was no change in the size or thickness of the lesions until she reached 10 years of age. Two months later, the patient started systemic everolimus (5 mg, AFINITOR®, Novartis, Basel, Switzerland) treatment for 17 months under the care of a pediatric neurologist for seizure control. Subsequent fundus examination and measurements by optical coherence tomography showed improvement in the maximal thickness of all lesions, specifically, a reduction of 25%.
Conclusions
mTOR inhibitors are targeted agents that regress systemic hamartomas and control convulsions without serious side effects in TSC patients. The particular one used in this study, Afinitor everolimus, reduced the RAH size in our patient. Thus, in cases where an RAH affects vision due to its location, everolimus can considered as a therapeutic option.
결절경화증은 상염색체 우성 유성질환으로 약 6,000명에서 한 명 꼴로 발생하며, TSC`(9q34)/TSC2(16p13) 유전자의 변이에 의해 발생한다고 알려져 있다[1]. 이로 인해 mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) 신호체계의 과다활동이 일어나며, 세포 성장과 사멸에 관여하는 조절기전에 이상이 생기고 망막을 포함한 심장, 신장 등 여러 기관에 과오종이 생기는 등 다양한 임상양상이 특징적으로 나타난다[2]. 현재 mTOR를 선택적으로 억제하는 rapamycin과 everolimus는 불응성 간질(refractory epilepsy)을 비롯한 결절경화증 환자의 전신병변에 효과적인 표적치료제로 사용되고 있다[3].
망막의 성상세포과오종은 결절경화증 환자의 40-50%에서 나타나는데 대부분 무증상이고 병변의 크기가 커지지 않고 안정적인 경우가 많으나[4], 크기가 큰 경우 망막내/망막하삼출을 일으켜 시력저하를 유발할 수 있고, 일부 병변은 크기가 점점 커질 수 있어 주의깊은 경과 관찰이 필요하다. 이에 비해 병변의 자연적인 호전은 매우 드문 것으로 알려져 있는데[3], 최근 레이저, 유리체강내 주사로 호전되지 않았던 망막 성상세포과오종의 두께와 크기가 rapamycin, everolimus 전신 투여 후 감소되고 시력호전을 보인 예가 국외에서 보고되고 있으나[5-7], 국내에서는 아직까지 보고된 바가 없다. 이에 저자들은 결절경화증 환자의 초진 후 10년간 변화를 보이지 않았으나 everolimus 투여 후 망막성상세포과오종의 두께가 감소한 것을 경험하였기에 이를 보고하는 바이다.
증례보고
결절경화증으로 진단받고 생후 3개월경 안과 검진을 통해 양안의 다발성 망막성상세포 과오종이 발견된 후 1년마다 경과 관찰 중인 12세 여아가 정기적 안저검사를 위해 내원하였다. 환아의 아버지가 결절경화증으로 진단받았다. 환아는 임신 41주에 제왕절개로 분만되었으며, 임신 28주경 산전초음파에서 좌심실내 종괴가 확인되었다. 출생 직후 동반 질환 확인을 위해 촬영한 두부 자기공명영상에서 다수의 뇌실막밑 결절 및 백질 이상, 겉질 융기 소견이 있었으며(Fig. 1), 얼굴, 목, 배, 다리에 특징적인 저색소 병변과 피지선종이 있어 결절경화증으로 진단되었다. 생후 4개월부터 영아연축이 있어 vigabatrin, clonazepam을 3년간 복용하였고 추가 경련이 없어서 해당 약제를 중단하였다.
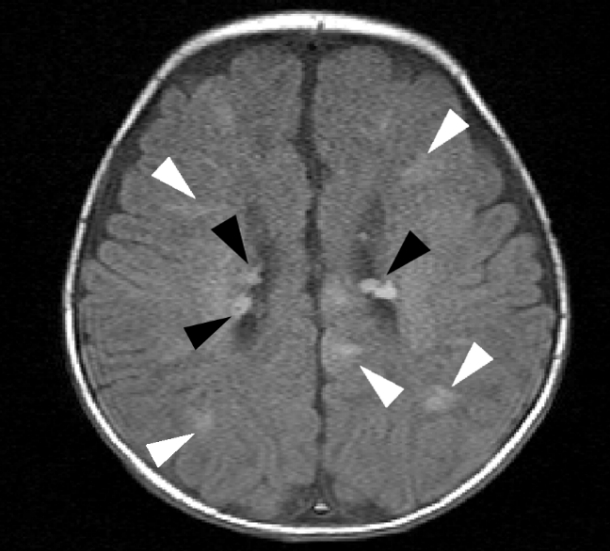
Brain magnetic resonance imaging image which was obtained immediately after birth. On Axial T1-weighted image, multiple subependymal nodule (black arrowheads) are located lateral ventricle behind the foramen Monro, in high signinal intensity without enhancement. There are several white matter abnormalities and cortical tubers that extend from the ventricle through the cerebrum toward the cortex (white arrowheads), representing tuberous sclerosis.
생후 3개월 경 초진시 정상 눈맞춤, 따라보기가 가능하였으며 굴절검사에서 우안 +1.50 Dsph, 좌안 +2.00 Dsph 원시가 보였고 사시는 없었다. 우안 시신경유두 상측, 상이측에 반투명한 회색을 띤 융기된 병변이 2개, 좌안 시신경유두 비측에 연접한 1유두직경크기의 융기된 병변과 부분적인 동맥 혈관초(sheathing), 시신경유두 비측의 회색으로 융기된 1유두직경크기의 병변 1개가 관찰되었다(Fig. 2A, B).
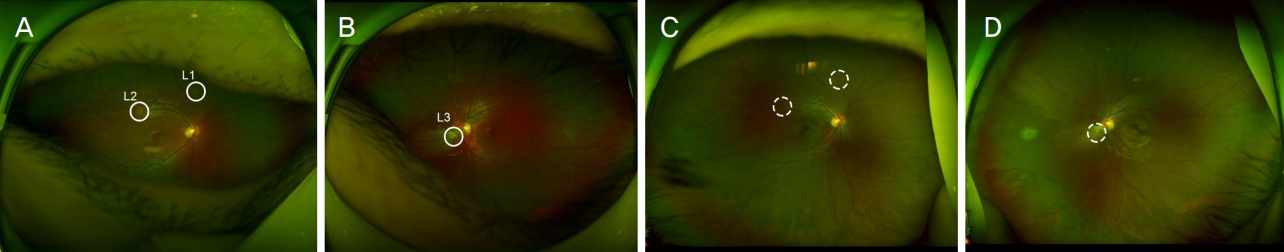
Wide fundus photography of regressed multiple retinal astrocytic hamartomas before and after everolimus treatment. (A, B) Two months before treatment, (C, D) 17 months after treatment initiation. L1, 2, 3 representated lesion 1, 2, 3 respectively, the solid circles on (A, B) are lesion before treatment, the dotted circles on (C, D) are identical location with solid circle, after treatment.
초진 이후 약 3개월-1년 간격으로 시행한 안저검사에서 양안 망막의 과오종 크기 및 위치는 큰 변화를 보이지 않았다. 만 10세경 검진시 양안 나안시력 1.0, 동공반응 정상, 전안부검사상 특이 소견은 없었으며 굴절검사상 우안 +0.50 Dsph, 좌안 +0.75 Dsph의 경도 원시 소견이었다.
안저 소견은 만 9세경 검사와 동일하였다. 빛간섭단층촬영에서 과오종은 망막 신경섬유층에 한정된 돔 형태의 고반사층이 나타났으며 정상망막과의 점진적인 경계를 가지고 있었다. 검진 2개월 후 비전형적 뇌파가 동반된 경련을 하여소아신경과에서 oxcarbazepine (Trileptal® Novartis, Basel, Switzerland) 900 mg 및 everolimus (Afinitor® Novartis, Basel, Switzerland) 5 mg을 처방하였으며, 이후 경련은 호전되었고 얼굴 및 손의 피지선종 크기가 50% 이상 감소하였다. 설사, 혈당상승, 아프타 궤양과 같은 약물치료와 관련된 부작용은 발생하지 않았다. 약 17개월간 약제 복용 후 만 12세에 시행한 안과 검진에서 교정시력 우안(1.0) × -2.25 Dsph, 좌안 (1.0) × -2.25 Dsph -0.25Dcyl axis 170로 근시 변화가 있었다. 안저 소견 및 빛간섭단층촬영상 19개월 전에 비해 망막 과오종의 두께가 감소하였다(Fig. 2C, D). 빛간섭단층촬영에서 높이를 3회 이상 측정할 수 있었던 3개 병변의 가장 높은 두께를 측정하였을 때, 치료 전 750, 654, 626 μm에서 치료 후 452, 569, 480 μm로 감소하여, 평균 25.3%의 감소를 보였다(Fig. 3, 4).
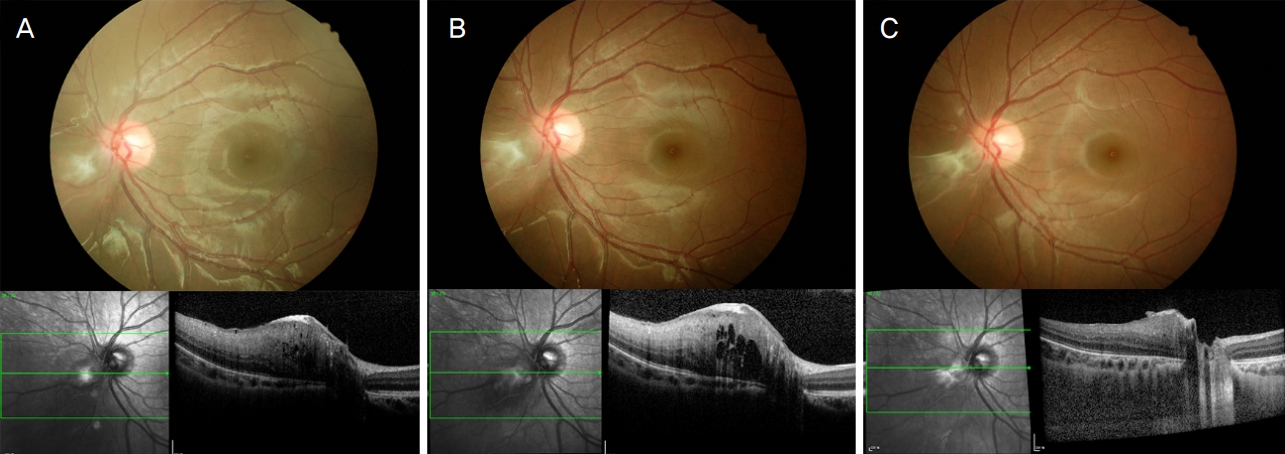
Representative serial images of retinal astrocytic hamartomas lesion borders the inferotemporal edge of the optic nerve in left eye with everolimus treatment (L3, the location was pointed out at Fig. 2). The maximal thickness of lesion showed 40% reduction after treatment compare to initial examination. Fundus photo (upper) and optical coherence tomograph image (lower). (A) Initial appearance, (B) 2 months before treatment (2019. 3), (C) 17 months after treatment initiation.
고 찰
망막성상세포과오종은 결절경화증 환자에서 나타나는 눈 병변 중 가장 흔한 형태로, 환자의 40-50%에서 발생하지만 대부분 진행하지 않으며, 시력에 영향을 미치지 않아 치료가 필요하지 않는다[4,8,9]. 그러나 병변이 후극부에 위치하거나 시신경유두와 연접한 경우 중심시력저하를 일으킬 수 있으며, 드물게 크기가 빠르게 증가하는 경우 이차 망막박리와 녹내장의 합병증을 일으켜 안구적출을 시행한 국내외의 보고가 있고[10-12], 국내에서는 크기 성장에 따른 망막신경섬유층의 결손 또한 보고된 바 있다[13]. 따라서 결절경화증 환아에서 주기적인 안과검진은 필수적이며, 위치나 크기 변화에 따라 치료가 필요한 경우 안구내 종양에 대한 고식적 치료인 광역학치료(photodynamic therapy), 열치료(transpupillary thermotherapy), 유리체강내 주사 등이 시도되고 있으나[10,14,15] 병변의 크기나 두께를 감소시키기 위한 명확한 치료법은 현재 없다.
Sirolimus와 everolimus는 FK506 binding protein 12와 mTOR의 결합시켜 mTOR kinase와 결합하지 못하게 함으로써 mTOR complex 1의 기능을 억제시킨다[6]. 이는 결절경화증 환자의 특이적인 유전적 결함을 표적으로 하여 치료효과를 나타내는 것으로, Zhang et al [7]의 연구에서 무증상의 성인 환자를 대상으로 sirolimus를 8개월간 복용한 경우 약 13.9%, everolimus를 복용한 경우 39.6%의 두께 감소를 보였다. 다수의 망막과오종이 확인된 결절경화증 환자 8명, 16안을 대상으로 전향적으로 everolimus를 6개월간 투여하고 그 차이를 분석한 최근의 연구[5]에서는, 병변의 두께가 평균 15.5% 감소하였고 특히 과오종의 형태적 분류에 따라 치료 반응에 차이를 보이는데 Type I (회색의 반투명한 색깔을 띠는 납작한 종괴로서 망막신경세포층 내에 국한되어 있고, 석회화를 동반하지 않는 병변)이 Type II (뽕나무 열매 모양으로 다수의 결절을 가지는 석회화된 병변) 병변보다 두께가 더 많이 감소하였다고 하였다. 또한 Nallasamy et al [6]은 13개월 영아에서 고식적 치료에 반응하지 않는 후 극부에 위치하고 빠르게 성장하는 망막성상세포종을 치료하기 위한 목적으로 everolimus를 2 mg/day로 시작하여 환아의 전신적 성장과 치료 효과에 따라 5 mg/day까지 증량하고 12개월간 유지한 결과 망막의 병변과 함께 두개강내 뇌실막밑 결절, 신장 낭종과 심장의 횡문근종 또한 호전 양상을 보였다고 보고하였다. 주목할 만한 점은 치료 효과가 첫 한 달에 최고에 달한 후 이후에는 유지되는 경향을 보이며 용량에 따라 치료 효과도 비례한다는 것이다.
본 증례에서 나타난 망막 과오종은 everolimus에 반응이 좋은 Type I에 해당하며, 16개월간의 치료 후 초기 치료 목적이었던 불응성 경련을 포함하여 망막의 과오종, 얼굴과 손의 피지선종까지 모두 호전을 보였다. 또한 부작용인 설사, 혈당상승, 아프타궤양 등을 포함한 치료 후 불편, 부작용도 없었다. 크기의 감소는 안저사진과 빛간섭단층촬영을 통해 정량적으로 증명되었으며, 이는 everolimus가 망막혈액 순환까지 도달하여 결절경화증 환자에서 망막과오종을 표적으로 한 치료가 가능하다는 것을 시사한다. 본 증례는 표적치료 후 호전된 망막과오종의 국내 첫 보고이며, 후극부나 시신경유두 주변에 발생하여 시력과 시야에 영향을 주는 과오종의 경우 everolimus를 치료적 수단으로 고려할 수 있겠다.
Notes
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
References
Biography
김현아 / Hyuna Kim
순천향대학교 의과대학 서울병원 안과학교실
Department of Ophthalmology, Soonchunhyang University Seoul Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine