분자유전검사로 확진된 상염색체 우성 드루젠
Autosomal Dominant Drusen Confirmed by Molecular Genetics
Article information
Abstract
목적
분자유전검사로 확진된 상염색체 우성 드루젠 1예를 경험하여 이의 임상적 특징 및 여러 진단적 이미지 검사 소견들을 보고하고자 한다.
증례요약
32세 남성이 1년 전부터 시작된 우안 시력저하를 주소로 내원하였다. 나안시력 우안 0.3, 좌안 1.2였고, 안저검사상 양안 후극부에 광범위하게 분포한 다양한 크기의 수많은 드루젠 및 우안 황반부의 망막하 섬유화 변화와 색소침착이 관찰되었다. 빛간섭단층촬영상 양안 망막색소상피층하 광범위한 고반사 물질의 침착과 우안 소량의 망막내액이 관찰되었다. 이 침착물은 형광안저혈관조영술상 과형광, 인도시아닌그린혈관조영술상 저형광, 안저자가형광검사상 과형광 반점 소견으로 관찰되었다. 분자유전검사 결과 EFEMP1 유전자의 병원성 변이인 이형 접합 c.1033C>T p.Arg345Trp이 검출되어 상염색체 우성 드루젠으로 확진할 수 있었다. 우안 아바스틴 주입술을 시행하였으나, 주사 후 망막내액 및 시력의 호전은 없었다.
결론
상염색체 우성 드루젠은 매우 드문 질환이나, 일반적인 나이관련황반변성과는 호발 연령 및 드루젠의 임상 양상이 다르고, 항혈관내피성장인자 치료의 반응 또한 차이를 보일 수 있어 감별이 필요하다.
Trans Abstract
Purpose
To report a case of autosomal dominant drusen confirmed by molecular genetic testing and the clinical features and findings of a multimodal diagnostic imaging study.
Case summary
A 32-year-old male presented with decreased visual acuity in his right eye from 1 year prior to his first visit. On the first visit, his visual acuities were 0.3 in the right eye and 1.2 in the left eye. A fundus examination showed numerous drusen of various sizes widely distributed on the posterior pole of both eyes, as well as subretinal fibrotic change with pigmentation in the right eye. Optical coherence tomography showed extensive hyperreflective deposits beneath the retinal pigment epithelium in both eyes and small amounts of cystic intraretinal fluid in the right eye. Fluorescein angiography and fundus autofluorescence showed the drusen as multiple hyperfluorescent spots, while indocyanine green angiography indicated hypofluorescence corresponding to the drusen. Genetic sequence analysis revealed a pathogenic variant of the EFEMP1 gene, heterozygous c.1033C>T (p.Arg345Trp), which accords with the diagnosis of autosomal dominant drusen. Intravitreal bevacizumab injection was given in the right eye; however, there was no improvement in the amount of intraretinal fluid nor visual acuity.
Conclusions
Autosomal dominant drusen is a very rare disease. It is necessary to distinguish it from age-related macular degeneration, as the affected age and clinical features of drusen are different, including the response to anti-vascular endothelial growth factor treatment.
상염색체 우성 드루젠(autosomal dominant drusen)은 Malattia leventinese 또는 Doyne honeycomb retinal dystrophy라고도 불리우는 질환으로, 상염색체 우성으로 유전되며 진행성 중심시력 상실을 일으키는 매우 드문 망막질환이다. 작은 원형의 황백색 망막반점들이 황반 부위 및 시신경유두 주위에 분포하여 결국 벌집 모양으로 형성되는 안저 소견을 특징으로 하며, 현재까지 진행된 유전자 연구에 의하면 EGF-containing fibrillin-like extracellular matrix protein (EFEMP1) 유전자의 단일 과오 돌연변이(Arg345Trp)에 기인하는 것으로 밝혀진 바 있다[1]. EFEMP1는 fibulin-3이라는 단백질을 암호화하며, 이는 망막드루젠 형성 및 황반변성의 병인에 관계된 망막의 세포외기질을 구성하고 있는 단백질이다. 유전자 돌연변이로 인한 fibulin-3의 잘못된 접힘(protein misfolding) 및 비효율적 분비로 망막색소상피층(retinal pigment epithelium)과 브루크막 사이에 생긴 축적물이 드루젠을 생성하게 된다[1]. 현재까지 레이저 치료 및 항혈관내피성장인자 치료들이 시도되었으나, 이러한 유전자 돌연변이로 인한 상태를 교정하는 효과적인 방법은 없다.
상염색체 우성 드루젠의 임상양상과 유전자 분석에 대한 보고는 국외의 증례보고가 있지만, 현재까지 국내에서는 보고된 바가 없다. 저자들은 임상적으로 진단되고 분자유전검사로 확진된 상염색체 우성 드루젠 1예를 경험하였기에, 다양한 진단적 이미지 검사 소견과 함께 이를 보고하고자 한다.
증례보고
32세 우즈베키스탄인 남자 환자가 1년 전부터 지속되는 우안 시력저하를 주소로 내원하였다. 당뇨병이나 고혈압 등의 기저질환은 없었으며, 안과적 질환에 대한 가족력은 부인하였다. 초진시 나안시력은 우안 0.3, 좌안 1.2였고, 세극등현미경검사에서 양안 모두 전안부에 특이 소견은 관찰되지 않았다. 안저검사에서 양안의 후극부 및 시신경유두 주위로 넓게 퍼진 융합하는 모양의 수많은 크기가 다양한 황백색 반점들이 관찰되었고, 우안에는 황반부의 섬유화 변화와 색소침착을 동반한 흉터성 변화도 함께 보였다(Figure 1A, B). 빛간섭단층촬영(optical coherence tomography) 상 양안 망막색소상피층 아래의 광범위한 고반사성 물질이 마치 물결 모양처럼 관찰되며 망막색소상피층과 브루크막 사이 층이 고반사성 물질의 축적으로 인해 두꺼워져 있는 것을 관찰할 수 있다. 좌안은 중심와 영역의 광수용체를 포함한 감각신경망막(neurosensory retina)이 잘 보존되어 있었으나, 우안은 중심와를 포함한 후극부에 전반적인 빛수용체내외절이음부(photoreceptor inner segment/outer segment junction)의 소실과 함께 소량의 수포망막내액이 관찰되었다(Figure 1C, D). 안저자가형광검사(fundus autofluorescence) 상 안저검사에서 보인 후극부의 중간 및 큰 드루젠은 과형광 소견을 보였고, 우안의 황반부 섬유화 병소는 저형광으로 나타났다(Figure 1E, F).
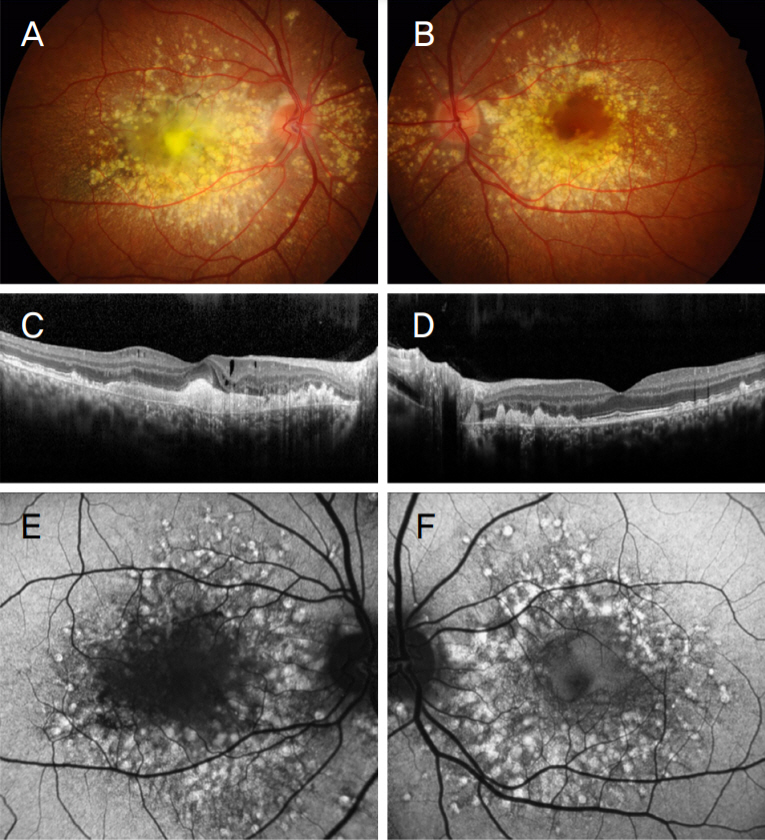
Fundus photography, optical coherence tomography and fundus autofluorescence of autosomal dominant drusen. (A, B) Fundus photographs show diffuse and confluent drusen with variable size, widely distributed in the posterior pole and peripapillary area. (C, D) Optical coherence tomography reveals bilateral extensive hyperreflective thickening beneath the retinal pigment epithelium accompanied by wavy uplift and intraretinal fluid of the right eye. (E, F) Fundus autofluorescence shows hyperautofluorescent spots corresponding to large drusen.
형광안저혈관조영술(fluorescein angiography)상 드루젠은 초기에서 후기로 갈수록 과형광이 증가하나 형광누출은 관찰되지 않았고(Figure 2A-D), 인도시아닌 그린혈관조영술(indocyanine green angiography)에서는 중심부의 크기가 큰 드루젠은 저형광 소견으로, 주변부의 크기가 작은 드루젠은 과형광 소견으로 나타나는 양상을 보였다(Figure 2E, F). 빛간섭단층혈관조영술(optical coherence tomography angiography)에서는 망막의 표층부터 심부까지의 혈관, 그리고 맥락막혈관 분포에서 특징적인 혈관 변화 양상 및 신생혈관 소견은 관찰되지 않았으며, 큰 드루젠이 있는 곳에서는 특히 맥락막모세혈관층에서 그림자 효과로 인한 저형광 영역이 생기는 것을 관찰할 수 있었다. 정면빛간섭단층혈관조영술(en face optical coherence tomography angiography) 이미지에서 심부 망막층부터 바깥망막층 및 맥락막모세혈관층까지 드루젠이 있는 영역에서 고반사성으로 밝게 나타나 특징적인 벌집모양 양상을 보였다(Figure 3).
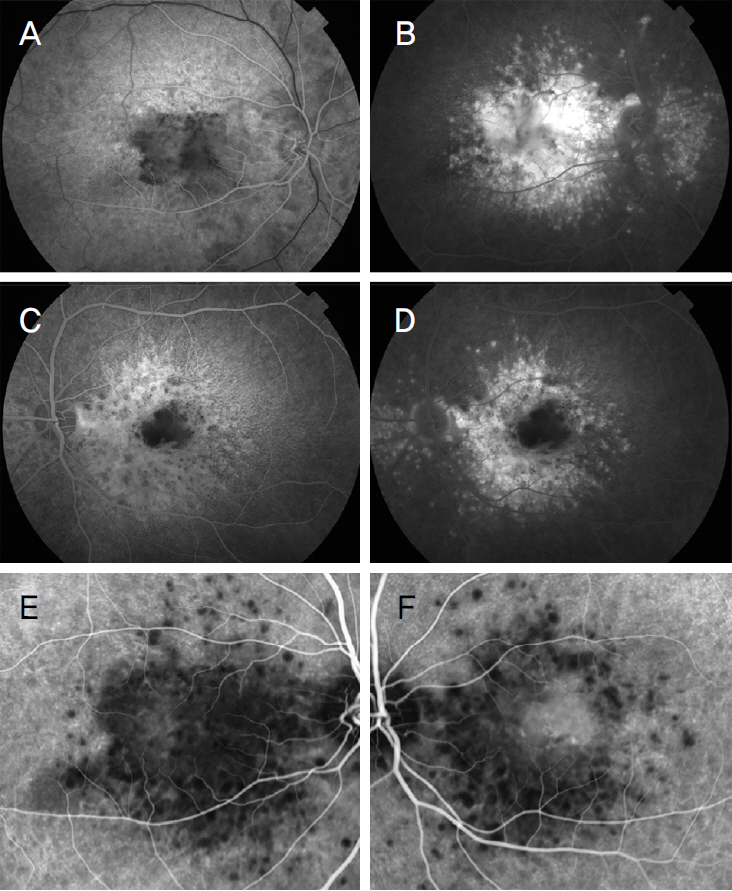
Fluorescein angiography and indocyanine green angiography of autosomal dominant drusen. (A, C) In the early phase of fluorescein angiography, indistinct hypofluorescence corresponding to large drusen and diffuse pinpoint hyperfluorescence corresponding to small drusen are noticed. (B, D) In the late phase of fluorescein angiography, ill-defined zone of hyperfluorescence corresponding to large drusen and less intense hyperfluorescence of the small drusen are visible. (E, F) Indocyanine green angiography reveals multiple hypofluorescent dots corresponding to large drusen with small hyperfluorescent spots of the small drusen.
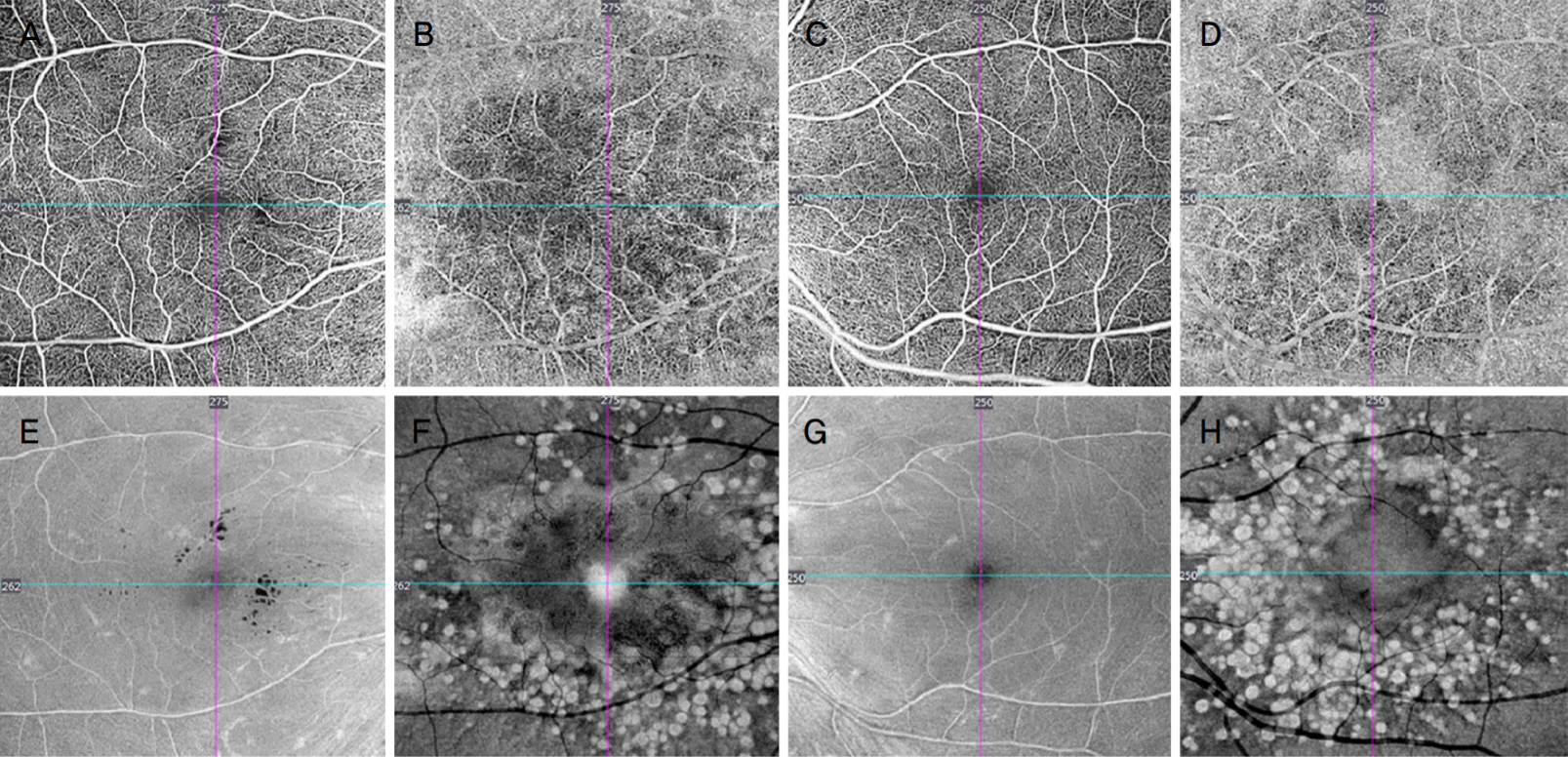
Optical coherence tomography angiography of autosomal dominant drusen. Each figure represents the slab of the corresponding layer. (A, C) superficial capillary plexus (SCP), (B, D) outer retina-choroid complex (ORCC), (E, G) en face images segmented at the level of the SCP, (F, H) en face images segmented at the level of the ORCC. Choroidal neovascularization was not observed in both eyes. The distribution pattern of drusen is more visible in the en face ORCC slab, while the cystic intraretinal fluid of the right eye is better seen in the en face SCP slab.
전영역 망막전위도검사(full-field electroretinography)에서는 암순응검사시 간상세포 반응 및 간상세포-원뿔세포 복합 반응에서 양안 모두 정상적인 a-wave 및 b-wave의 진폭 및 정적잠시(implicit time)를 보였고, 명순응검사에서도 원뿔세포 반응은 a-wave 및 b-wave 모두 특징적인 이상 소견은 보이지 않았다. 30-Hz flicker 반응에서 우안이 좌안에 비해 진폭이 다소 작았으나 정상 범위 이내였다(Figure 4A). 골드만시야계검사(Goldmann visual field test)에서 우안의 중심암점 외에는 특이 소견이 관찰되지 않았다(Figure 4B). 눈전위도검사(electrooculogram)에서 Arden 비는 양안 모두 2.3으로 정상 소견이었다.
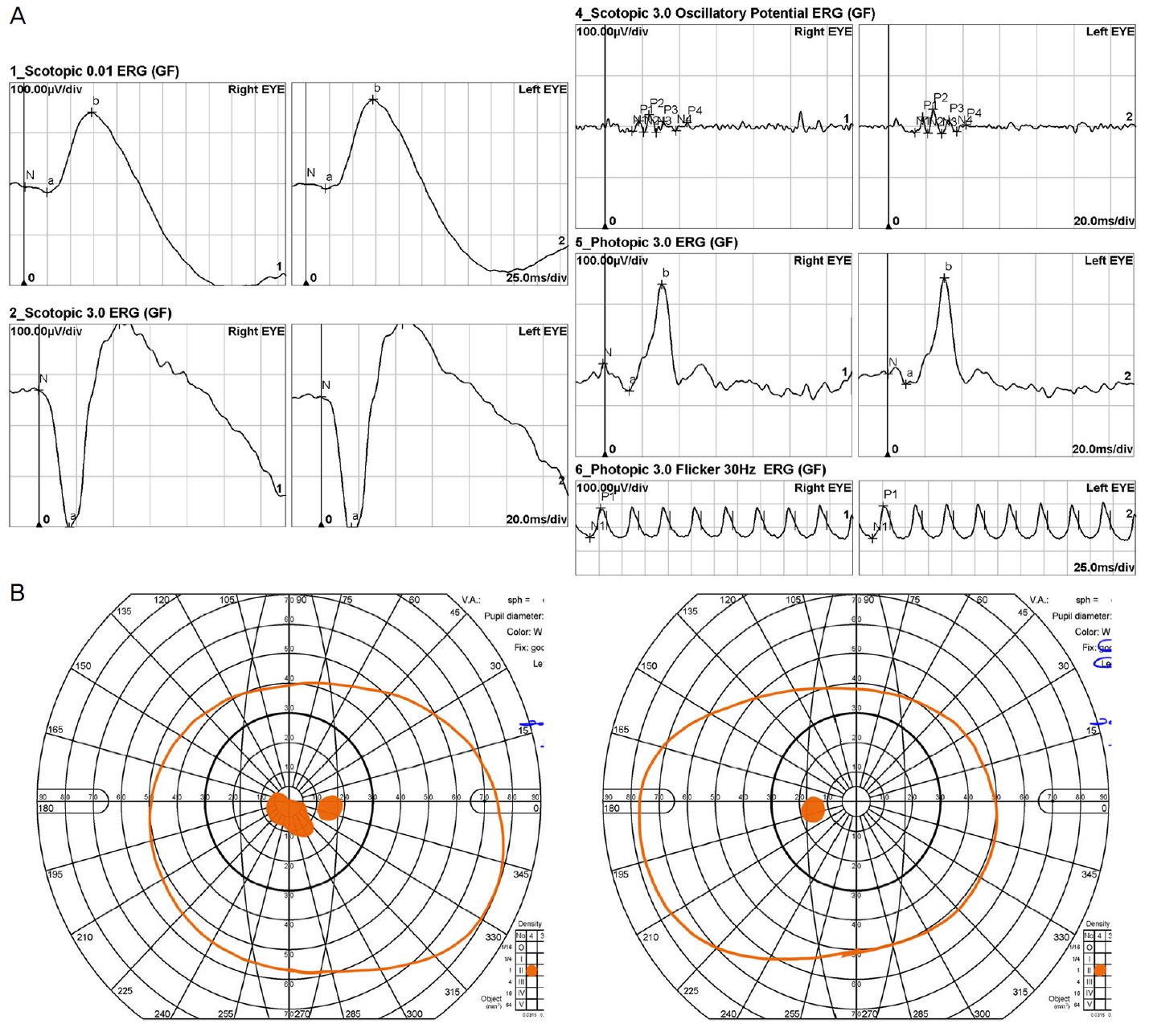
Functional tests of autosomal dominant drusen. (A) Full-field electroretinography showed normal rod and cone responses, while 30-Hz flicker response was marginally reduced in the right eye. (B) Goldmann visual field test showed central scotoma in the right eye.
이에 임상양상을 통해 상염색체 우성 드루젠으로 진단하고, 엑솜 염기서열분석(exome sequencing)을 진행하였다. 환자에게 동의를 구한 뒤 채취한 환자의 혈액 샘플에서 SureSelectXT Human all Exon 50 Mb Kit (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA)를 사용하여 유전체 DNA를 추출하여 정제하였고, Illumina Multiplexing Sample Preparation Oligonucleotide Kit와 HiSeq 2000 Paired-End Cluster Generation Kit를 이용한 HiSeq 2000 system (Illumina, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA)을 사용하여 엑솜 샘플의 증폭 및 염기서열 분석을 시행하였다. 2015 American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics guidelines을 토대로 염기서열분석을 시행한 결과 EFEMP1 유전자에 대하여 병원성 변이형(pathogenic variants)인 NM_001039348.2: c.1033C>T (p.Arg345Trp) 이형 접합체(heterozygote)가 검출되어 상염색체 우성 드루젠으로 확진하였다.
초진 한 달 반 뒤에 환자는 다시 내원하였고, 우안 시력은 0.2, 좌안은 1.2로 측정되었다. 시행한 다면적 검사에서, 명확한 맥락막신생혈관은 확인되지 않았으나 빛간섭단층 촬영상 우안의 망막내액이 여전히 관찰되어 유리체강내 베바시주맙(Avastin®; Genetech, South San Francisco, CA, USA) 주사를 시행하였다. 주사 한 달 반 후 내원시 우안 시력 0.2, 좌안 1.5로 측정되었으며, 양안 안저 소견의 명확한 변화는 없었고, 빛간섭단층촬영에서 우안 망막내액의 감소는 관찰되지 않았다.
고 찰
상염색체 우성 드루젠은 1899년 Doyne [2]에 의해 처음 보고되었으며, 황반부의 드루젠이 모자이크 형태로 형성되어 마치 ‘벌집 모양’을 보인다고 하여 Doyne honeycomb retinal dystrophy라고 불리웠다. 이후 1925년 Vogt [3]는 스위스 남부의 Leventine valley에 거주하는 환자들에서 특징적으로 드루젠이 방사형으로 분포하는 양상을 보여 Malattia leventinese라고 보고한다. 이후 1999년이 되어서야 Stone et al [1]은 두 질환이 모두 EFEMP1 유전자의 단일점 돌연변이(single point mutation, Arg345Trp)에 의해 유발된 하나의 질환임을 밝혔다. 이에 질환에 대한 여러 이름이 병용되어 쓰이나, 본 증례보고에서는 상염색체 우성 드루젠(autosomal dominant drusen)이라고 지칭했다. 상염색체 우성 드루젠은 세계적으로 매우 드물게 보고된 바 있고, 특히 다방면의 안과검사들을 시행한 유전자검사로 확진된 경우는 현재까지 국내에 보고된 증례가 없다. 본 증례는 상염색체 우성 드루젠으로 진단된 환자의 다양한 진단적 이미지 검사 소견 및 임상경과, 그리고 분자유전검사 결과에 대해 보고하는 바 이다.
본 증례 환자의 안저 소견은 후극부 및 시신경유두 주변 수많은 드루젠들이 관찰되는 상염색체 우성 드루젠의 전형적인 모습을 보여주고 있으며, 이는 나이관련황반변성(age-related macular degeneration)에서 관찰되는 드루젠과 비슷한 양상을 보이기에 감별하는 것이 중요하다. 먼저, 발병 연령에서 차이가 있을 수 있는데, 상염색체 우성 드루젠은 보통 30대에서 40대 나이에 변시증 혹은 시력저하를 호소하게 되며, 전형적인 나이관련황반변성에 비해 비교적 더 젊은 나이에서 호발한다. 하지만 일부 상염색체 우성 드루젠 환자에서 노년기까지 증상이 없는 경우도 있다. 또한, 드루젠의 특징과 분포에 있어서도 상염색체 우성 드루젠은 나이관련황반변성과 차이를 보인다. 황반 중심과 시신경유두의 비측 경계에 크기가 크고 동그란 모양의 드루젠이 관찰되며 이들은 주로 융합되어 벌집 모양으로 나타나고, 시간이 지남에 따라 색소침착과 망막색소상피 위축이 동반되기도 한다. 황반 이측을 중심으로 방사상으로 분포하는 드루젠은 보다 크기가 작고, 얇고 길쭉한 모양으로 나타난다.
빛간섭단층촬영을 이용한 이전 연구에서 이 질환에서 나타나는 드루젠을 망막색소상피층 아래에 넓게 퍼져있거나 국소적 돔 모양으로 존재하는 고반사성의 큰 드루젠과 망막색소상피층 위쪽으로 마치 톱니 모양처럼 나타나는 작은 드루젠 두 가지 종류로 분류하여 설명하고 있다[4]. 큰 드루젠은 빛수용체내외절이음부의 손상이 동반되나 작은 드루젠은 보존되어 있으며, 이 작은 드루젠은 표층 드루젠(cuticular drusen)과 유사한 양상을 보인다는 것도 보고된 바 있다[5]. 안저자가형광검사에서 Querques et al [4]은 큰 드루젠이 증가된 자가형광 소견을 보이는 것에 반해, 작은 드루젠에서는 오히려 감소되거나 보이지 않는다고 보고하였고, 본 증례에서도 같은 소견을 관찰할 수 있었다. 큰 드루젠에서 증가된 자가형광 소견을 보이는 것은 전형적인 나이관련황반변성의 드루젠이 저형광을 보이는 것과 구별되는 또 하나의 특징이다. 형광안저혈관조영술과 인도시아닌그린혈관조영술을 통해 두 종류의 드루젠의 형태적, 기능적 차이를 추가로 볼 수 있다. Souied et al [6]은 인도시아닌그린혈관조영술에서 큰 드루젠은 초기에 저형광을 보이다가, 후기에는 저형광의 테두리(hypofluorescent halos)를 가진 과형광 반점으로 보인다 하였고, 작은 드루젠은 대부분 과형광으로 나타나고 후기로 갈수록 그 형광이 감소하는 양상을 보인다고 밝혔다. 형광안저혈관조영술에서는 큰 드루젠은 초기에 뚜렷하지 않거나 저형광 소견으로 관찰되다가, 후기로 갈수록 경계가 불분명한 과형광의 염색(hyperfluorescent staining)으로 나타났고, 작은 드루젠은 초기에 경계가 분명한 과형광으로 보이다가 후기로 갈수록 그 형광이 감소하는 양상을 보였다고 보고했다.
본 증례에서는 빛간섭단층혈관조영술검사상 뚜렷한 맥락막신생혈관을 발견할 수 없었으나, 이전 보고에서 상염색체 우성 드루젠 환자에서 기존 검사 장비로 발견되지 못한 맥락막신생혈관을 빛간섭단층혈관조영술을 이용하여 발견할 수 있었다고 밝힌 바 있다[7]. 질환의 후기에 발생 가능한 이 맥락막신생혈관은 이전의 여러 보고에서 심각한 시력 손실을 일으킬 수 있다고 보고되었다[8,9]. 이는 나이관련황반변성에서 나타나는 맥락막신생혈관의 표현형과 유사성을 보여 유리체강내 항혈관내피성장인자 주사 치료가 시도되어 왔고, Sohn et al [10]은 맥락막신생혈관을 보인 2명의 상염색체 우성 드루젠 환자에서 베바시주맙 주사 후 1명은 망막내액의 감소와 20/250에서 20/160으로 경도의 시력호전을, 다른 1명은 20/200에서 20/40으로의 시력호전을 보였다는 증례들을 보고하였다. Coates [11]는 맥락막신생혈관과 황반부종이 합병된 상염색체 우성 드루젠 환자에서, 항혈관내피성장인자 주사 치료 대신 경구 acetazolamide를 처방하였으며 망막내액의 감소를 경험한 증례를 보고하였다. 본 증례의 환자에서처럼 Ewe et al [12]은 맥락막신생혈관이 발견되지 않은 상태에서 망막하액이 발생한 상염색체 우성 드루젠 환자에서 맥락막신생혈관의 임상적인 의심하에 라니비주맙 주사 치료를 6개월간 시행하였고, 치료 결과 6/15에서 6/12로의 약간의 시력개선은 있었으나 망막하액은 변화가 없었다고 보고한 바 있다.
맥락막신생혈관이 동반되지 않은 상태에서 발생한 빛간섭단층촬영상의 저반사 수포망막내액에 대해 조직학적 연구 없이 그 기원을 명확히 알기는 어렵지만, 다음과 같이 추측해볼 수 있다. 광범위한 드루젠 침착물이 비가역적인 망막층의 구조적 손상(architectural disruptions)을 유발하고, 망막층에 가해진 물리적인 스트레스(mechanical stress)가 뮬러 세포의 전위(Müller cell displacement)를 초래하게 된다. 이러한 변화들로 인해 신경절세포층(ganglion cell layer), 내핵층(inner nuclear layer)에 빈 공간들이 생기게 되고, 이는 마치 X염색체관련소아망막층간분리나 베스트노른자모양황반이상증에서 관찰되는 낭포변성(cystic degeneration)과 유사한 양상의 저반사 수포망막내액을 초래하게 될 것이다. 본 증례의 환자가 형광안저혈관조영술상 전형적인 맥락막신생혈관의 누출을 발견할 수 없었다는 점과 베바시주맙 치료에도 불구하고 망막내액의 감소가 관찰되지 않는 점 등을 근거로, 이러한 낭포병변은 혈액망막장벽(blood retinal barrier)의 손상으로 혈관장애(vascular impairment)가 원인이 되어 발생하는 전형적인 삼출성(exudative) 황반부종과는 차이가 있을 것으로 생각된다.
이러한 환자들의 치료 결과에 대한 보고가 매우 제한적이므로, 빛간섭단층촬영에서 관찰되는 수포성 액체(cystic fluid)에 대한 치료 필요성에 대해 아직 합의된 의견은 없지만 다음과 같이 제안해볼 수 있다. 오랜 기간 안정적인 시력과 망막병소를 보이던 환자가 갑작스러운 시력저하를 호소하고, 빛간섭단층촬영상 새로이 발생한 액체가 있다면, 맥락막신생혈관의 가능성을 염두해 두고 항혈관내피성장인자 주사 치료를 고려해 볼 수 있겠다. 하지만 오랜 기간 악화되지 않고 안정적으로 유지되는 액체에 대해서는 낭포 변성의 가능성이 있다는 점, 항혈관내피성장인자 주사 치료에도 완전한 흡수가 어렵다는 점을 토대로 치료 없이 면밀한 경과 관찰을 해볼 수 있겠다.
Takeuchi et al [9]에 의하면 상염색체 우성 드루젠 환자에게 시행한 망막전위도검사에서 b-wave 및 간상세포-원뿔세포 복합 반응은 정상으로 보이고, 30-Hz flicker 반응은 감소했다고 보고하였고, Haimovici et al [13]은 황반부드루젠이 있는 곳에서는 암순응 감도의 감소 및 속도의 지연이 일어났다고 보고하였다. 본 증례에서도 망막전위도검사상 양안 모두 두드러진 파형의 지연 또는 진폭의 감소를 보이지는 않았다. 하지만 진행이 더 된 우안의 30-Hz flicker 반응의 진폭이 좌안에 비해 경미하게 감소되었으나(우안 124 μV, 좌안 135 μV) 정상 범위 내에 있었다. 이러한 결과를 종합해 보면 이 질환은 황반부의 넓은 영역에 분포하는 드루젠 침착물로 인해 불연속적인 국소 기능적 이상을 보여, 진행된 경과를 보일수록 전반적 기능 이상을 보이는 질환이라고 해석할 수 있을 것이다.
한편 분자유전학적 검사가 본 질환을 나이관련황반변성과 감별하는 데 도움이 된다. EFEMP1의 Arg345Trp 돌연변이는 나이관련황반변성과는 연관이 없다는 것이 보고된 바 있으며[14], 상염색체 우성 드루젠은 현재까지 보고된 모든 사례에서 해당 돌연변이가 발견되었다. 이를 통해 EFEMP1의 Arg345Trp 돌연변이가 특정한 표현형의 드루젠을 생성하는 데 기여할 것임을 유추해볼 수 있을 것이다. 또한 최근 연구에 따르면 면역조직화학분석에서도 상염색체 우성 드루젠과 나이관련황반변성에서의 드루젠의 차이가 있음을 밝힌 바 있다. 즉, 두 질환 모두 망막색소상피층과 브루크막 사이 기저 축적물(basal laminar deposits)들을 따라서 fibulin-3가 쌓이는 모습을 보이나[8], 상염색체 우성 드루젠의 드루젠에서는 나이관련황반변성의 드루젠에는 없는 콜라겐 IV형(collagen type IV)을 보유한 특이한 양파 껍질모양의 판층구조(onion skin-like lamination)를 보였다고 보고된 바 있다[15].
본 증례는 국내에서 상염색체 우성 드루젠을 분자유전검사로 확진한 첫 보고이며, 다양한 진단적 이미지 검사들의 소견에 대해 보고하였다. 상염색체 우성 드루젠은 매우 드문 질환이지만, 일반적인 나이관련황반변성과는 호발하는 연령 및 드루젠의 임상양상이 다르고, 유리체강내 항혈관내피성장인자 주사 치료의 반응 또한 차이를 보일 수 있어 감별하는 것이 필요하다고 사료된다.
Notes
Financial support: This research was supported by the Korean Association of Retinal Degeneration.
This study was presented as a poster at the 122nd Annual Meeting of the Korean Ophthalmological Society 2019.
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
References
Biography
송재신 / Jae Shin Song
서울대학교 의과대학 서울대학교병원 안과학교실
Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine
