상안정맥혈전증을 동반한 경동맥해면정맥동루
Carotid-cavernous Fistula Accompanied by Superior Ophthalmic Vein Thrombosis
Article information
Abstract
목적
안와연조직염으로 오인하였던 상안정맥혈전증을 동반한 경동맥해면정맥동루 1예를 보고하고자 한다.
증례요약
72세 여자 환자가 3일 전부터 점점 심해지는 좌안의 통증과 부종, 충혈을 주소로 타 병원에서 안와연조직염으로 진단받고 전원되었다. 왼쪽 눈꺼풀의 부종과 처짐, 결막의 심한 부종과 충혈이 있었다. 안구운동검사에서 좌안의 외전, 내전, 하전 장애를 보였고 복시를 호소하였다. 부비동 조영 컴퓨터단층촬영에서 좌안 상안검의 부종과 외안근 비대, 상안정맥의 확장과 혈전이 관찰되었다. 뇌자기공명촬영 및 자기공명혈관조영술에서 좌측의 경동맥해면정맥동루가 의심되어 신경외과로 전과되어 뇌혈관조영술을 시행하였고, 동측의 간접형 경동맥해면정맥동루와 반대측의 직접형 경동맥해면정맥동루가 확인되어 색전술 및 스텐트삽입술을 시행 받았다. 수술 후 7일째 눈꺼풀과 결막의 부종, 복시는 사라지고, 모든 방향에서 안구운동제한은 보이지 않았다.
결론
상안정맥혈전증은 안와연조직염과 같은 감염성 질환이 가장 흔한 원인으로 알려져 있으나 본 증례와 같이 경동맥해면정맥동루가 원인이 되는 경우도 있으므로 철저한 영상학적 검사가 증상의 빠른 호전에 중요하다.
Trans Abstract
Purpose
To report a case of carotid-cavernous fistula associated with superior ophthalmic vein thrombosis which was misdiagnosed as orbital cellulitis.
Case Summary
A 72-year-old female was transferred to our hospital because she had been diagnosed with orbital cellulitis at another hospital due to pain, swelling, and redness of the left eye, which became increasingly severe 3 days prior to her visit. The patient had edema and ptosis of the left eyelid, severe chemosis, and congestion of the conjunctiva. The eye movement test showed limitations in abduction, adduction, and infraduction of the left eye, and the patient complained of diplopia. Paranasal sinus computed tomography showed an edema of the left upper eyelid, enlargement of the extraocular muscles, and dilation and thrombosis of the superior ophthalmic vein. On brain magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance angiography, left carotid-cavernous fistula was suspected, so she was transferred to neurosurgery and a cerebral angiography was performed. Cerebral angiography showed an indirect carotid-cavernous fistula on the ipsilateral side and a direct carotid-cavernous fistula on the opposite side. The patient underwent embolization and stenting. Seven days after surgery, the eyelid and conjunctival swelling and diplopia disappeared and there was no limitation of eye movement in any direction.
Conclusions
An infectious disease such as orbital cellulitis is the most common cause of superior ophthalmic vein thrombosis. However, as in this patient, carotid-cavernous fistula can be the cause, so thorough imaging is important for rapid improvement of symptoms.
경동맥해면정맥동루(carotid-cavernous fistula)는 해면동으로부터 상안정맥으로의 역류성 혈류에 의한 안정맥 고혈압으로 인해 안와잡음, 안구돌출, 결막부종 및 충혈, 안압상승 등의 안와증상을 보인다[1]. 이러한 증상은 경동맥해면정맥동루가 생긴 동측의 안와에 관찰되는 경우가 가장 흔하지만 양측 해면정맥동의 연결에 의해 반대측에 안와증상을 보이기도 한다[2]. 경동맥해면정맥동루는 만성 결막염, 안와연조직염, 공막염, 상공막염 등으로 오진되는 경우가 많고 초진 시 바로 진단되는 경우는 드물다[3].
상안정맥혈전증(superior ophthalmic vein thrombosis)은 통증을 동반한 안구돌출, 결막 부종 및 충혈, 시력저하 등 경동맥해면정맥동루와 비슷한 임상증상을 공유하지만 증상 발생이 대부분 갑작스럽고, 드물지만 안면, 귀, 구강 등을 포함하는 부위에 치명적인 합병증을 남길 수 있는 해면정맥동 혈전증(cavernous sinus thrombosis)으로 진행이 될 수 있기 때문에 주의를 기울여야 한다. 상안정맥혈전증의 원인으로는 안와연조직염이 가장 흔하며, 안와종양, 경동맥해면정맥동루 등에서도 생길 수 있다[4]. 본 증례에서는 좌안의 통증과 부종, 충혈, 안구운동장애를 보인 환자에서 초진 시 안와연조직염으로 생각하였으나 국내에 증례가 보고된 적이 없는 상안정맥혈전증과 경동맥해면정맥동루가 함께 진단되어 색전술과 스텐트 치료로 완치된 증례를 경험하였기에 이를 보고하고자 한다.
증례요약
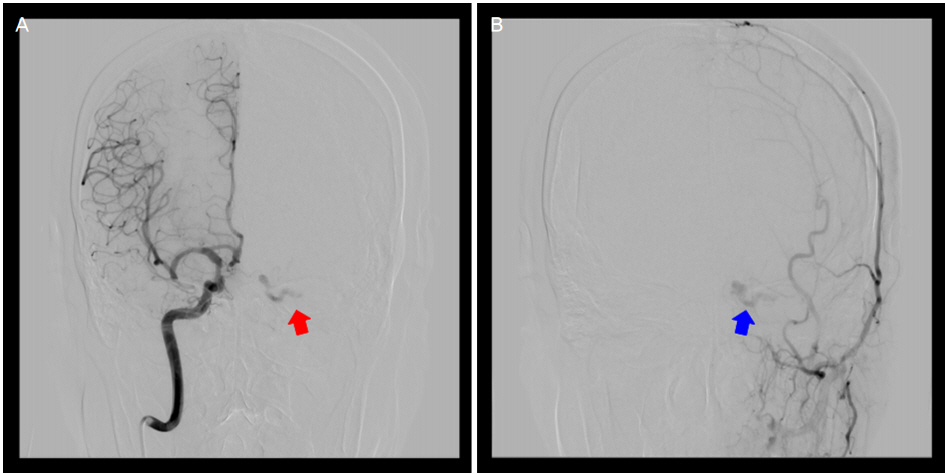
72세 여자 환자가 3일 전부터 점점 심해지는 좌안의 통증, 부종과 충혈을 주소로 타 병원에서 안와연조직염으로 진단받고 전원되었다. 알레르기 이외의 전신질환은 없었고 안과적 혹은 외상의 과거력은 없었다. 초진 시 최대교정시력은 우안 0.5 좌안 0.2, 안압은 우안 10 mmHg, 좌안 24 mmHg로 측정되었다. 왼쪽 눈꺼풀의 부종과 발적 및 처짐이 관찰되었으며, 결막의 심한 부종과 충혈이 보였다. 안와 주위로 잡음은 청진되지 않았으며 세극등검사상 양안의 중등도 노인성 백내장이 있었고, 각막과 전방 및 안저에서는 특이 소견을 보이지 않았다. 안구운동검사에서 좌안의 외전-3, 내전-2, 하전-2의 제한을 보였고 복시를 호소하였다(Fig. 1A). 전신 혈액검사에서 적혈구 침강 속도가 83 mm/hr로 상승되어 있었고 그 이외의 특이 소견은 없었다. 좌안의 안와연조직염 의심하에 입원하여 전신 항생제 치료를 계획하였고, 2세대 Cephalosporin과 Amikacin을 정맥주사하였다. 입원 후 촬영한 부비동 컴퓨터단층촬영 검사에서 좌안 상안검의 부종 및 지방조직의 침윤, 좌안의 외안근 비대와 안구돌출이 보였고 상안정맥의 확장과 함께 정맥 내 충만결손이 관찰되었다(Fig. 2). 좌안의 상안정맥혈전증으로 진단하였고, Aspirin 100 mg을 1일 1회 복용, Cilostazol (Pletaal®) 100 mg을 1일 2회 복용하도록 하였다. 뇌 자기공명촬영, 자기공명 혈관조영술에서 왼쪽의 전두안와 부위의 출혈(frontoorbital hemorrhage)과 경동맥해면정맥동루가 의심되는 병변을 보여 입원 후 6일째 항생제 투여는 중단하고 신경외과로 전과되었다. 입원 6일째 시행한 뇌혈관조영술에서 우측의 내경동맥과 좌측의 해면정맥동이 직접 연결되어 있는 직접형(direct-type)의 경동맥해면정맥동루와 좌측의 외경동맥 분지와 해면정맥동이 연결되어 있는 간접형(indirect [dural]-type)의 경동맥해면정맥동루가 발견되었다(Fig. 3). 우측의 경동맥해면정맥동루는 Low-profile Visualized Intraluminal Support (LVIS) 스텐트를 삽입하였고, 좌측의 경동맥해면정맥동루는 아교(glue)를 이용한 색전술을 시행하였다. 수술 후 7일째 최대교정시력은 좌안 0.5로 호전되었고 눈꺼풀과 결막의 부종은 완전히 사라지고 경도의 결막 충혈만 남았다. 안구운동검사에서 모든 방향에서 안구운동제한은 보이지 않았고 정위가 관찰되었으며 복시도 사라졌다(Fig. 1B).

Image of the patient in nine diagnostic position of gaze. (A) At initial visit, the patient showed edema and ptosis of the left eyelid, severe chemosis and congestion of the conjunctiva. Limitation of abduction, adduction, and infraduction were present in the left eye. (B) Seven days after surgery, eyelid swelling and conjunctival chemosis of the left eye were resolved and there was no limitation of eye movement in all directions.

Paranasal sinus computed tomography image of the patient. Axial and coronal view of paranasal sinus computed tomography shows engorgement of left superior ophthalmic vein with internal filling defect (red arrows) and soft tissue swelling in left periorbital area (A, B).
고 찰
경동맥해면정맥동루는 경동맥계와 해면정맥동 사이에 단락이 형성되어 비정상적 교통이 일어난 상태로 크게 외상성과 자발성으로 나눌 수 있고 해부학적 위치에 따라 직접형과 간접형(경막형)으로 구분할 수 있다. 직접형 경동맥해면정맥동루는 내경동맥과 해면정맥동이 직접적으로 연결된 상태로 주로 두개골절이나 수술적 외상에 의해 생길 수 있고 고혈류형 단락으로 인해 급격한 임상증상의 변화가 특징적이다[2]. 안 소견으로는 안구돌출, 결막충혈, 박동성 잡음이 대표적이며, 안와와 결막의 부종과 그로 인한 안구의 움직임 제한, 상공막정맥의 확장 등이 동반될 수 있다. 반면 간접형 경동맥해면정맥동루는 내경동맥 혹은 외경동맥의 뇌막분지와 해면정맥동이 간접적으로 연결된 상태로 대개 자발적으로 발생하며 증상이 경미하고 서서히 진행하여 만성결막염, 연조직염, 공막염, 상공막염, 안와종양, 가성종양 등으로 오진하여 치료가 지연되는 경우가 많다[5]. 경동맥해면정맥동루의 확실한 진단을 위해서는 뇌자기공명촬영, 뇌혈관조영술 등의 추가적인 영상학적 검사가 필요하다[3]. 경동맥해면정맥동루의 치료 목표는 완전한 누공의 폐쇄와 내경동맥의 혈류를 보전하는 것으로 누공부위의 혈관 색전술이 주 치료 방법이다. 증상이 경하거나 누출의 양이 적고, 자발적 폐쇄의 확률이 높은 경우에는 경부동정맥압박법을 시행할 수도 있다[6,7].
상안정맥혈전증은 상안정맥의 혈전 생성으로 인해 안와로부터의 정맥유출이 막힘으로 인하여 마비성 사시, 안와부종, 안구 돌출과 같은 증상이 급속히 진행하는 매우 드문 질환이다. 상안정맥혈전증의 병인은 다요인적이며 안와의 염증이나 감염, 응고 장애, 종양의 압박, 경동맥해면정맥동루 등에서 생길 수 있다. 특히 안와연조직염은 상안정맥혈전증의 제일 흔한 원인이지만 서로 비슷한 임상증상을 공유하기 때문에 감별을 꼭 해주어야 하는 질환이기도 하다[8]. 진단은 전산화단층촬영으로도 가능하지만, 질환의 초기에는 상안정맥의 확장과 감소된 혈류가 저명하지 않아 발견되지 않는 경우가 있고, 경동맥해면정맥동루, 해면정맥동혈전증, 부비동-안와 감염 등을 배제하기 위하여 뇌자기공명촬영 및 자기공명정맥조영술이 권유된다[9]. 치료는 항생제와 항응고제가 주된 치료로 안와 감염이 상안정맥혈전증의 가장 흔한 원인이기 때문에 경험적 항생제를 쓰는 것이 권유되며, Vancomycin과 Ceftazidime이 전형적으로 쓰인다. 항응고 치료에 대해서는 아직 논쟁이 있으나, 상안정맥혈전증이 해면정맥동 혈전증으로 진행할 가능성을 낮추기 위해 두개내 혹은 후복막 등의 출혈이 있는 금기증이 아니라면 사용하는 것이 좋다[10].
안와연조직염, 상안정맥혈전증, 경동맥해면정맥동루는 결막충혈, 안와 및 결막의 부종, 안구돌출 등 서로 유사한 임상증상을 공유하고 있지만 치료적 접근은 각기 다르기 때문에 초기에 철저한 평가를 하여 감별해야 한다. 본 증례의 환자는 초진 시에 안와연조직염을 의심하였고 염증의 파급 정도와 부비동에 대한 평가를 하기 위하여 부비동 컴퓨터단층촬영을 시행하였다. 컴퓨터단층촬영에서 보인 상안검의 부종과 지방조직 침윤 소견은 격막전 연조직염의 소견과 유사하였다. 그리고 상안정맥의 확장과 함께 혈전이 관찰되었으나 안와 내의 조영증강 및 염증 소견은 보이지 않았다. 안와연조직염이 상안정맥혈전증의 가장 흔한 원인이라고 알려져 있고, 안와로의 파급이 없는 격막전 연조직염만으로 상안정맥혈전증이 생겼다는 보고는 아직 없다. 해면동에 대한 평가를 위해 추가로 시행한 뇌자기공명촬영과 뇌혈관조영술에서 경동맥해면정맥동루가 진단이 되었고, 상안정맥의 혈전은 경동맥해면정맥동루로부터 생긴 것이라고 생각할 수 있었다. 또한 컴퓨터단층촬영에서 상안검의 부종과 지방조직 침윤 소견은 정맥고혈압에 의한 정맥울혈에 의해서도 유사하게 보일 수 있어서 실제로 안와연조직염이 동반되었을 가능성은 낮은 것으로 생각된다. 환자의 급작스러운 증상은 원래부터 있었던 경동맥해면정맥동루에서 혈류의 소용돌이가 발생하여 상안정맥 내의 혈전이 생겨 나타났을 것이라고 생각된다.
본 증례는 상안정맥혈전증과 동측의 간접형 경동맥해면정맥동루와 반대쪽의 직접형 경동맥해면정맥동루가 동시에 있었던 드문 경우이다. 특히 우측의 직접형 경동맥해면정맥동루의 경우 우측의 내경동맥이 해면사이정맥동을 통하여 직접 좌측의 해면정맥동으로 연결되어 우측의 증상 없이 좌측에만 증상을 나타낸 것으로 보인다. 경동맥해면 정맥동루와 상안정맥혈전증이 각각 언제 발생하였는지에 대해서는 알 수 없다. 저혈류 단락에 의해 증상이 경미하고 천천히 진행하는 간접형 경동맥해면정맥동루보다는 고혈류 단락에 의해 급성기 증상을 나타내는 직접형 경동맥해면정맥동루가 발생하면서 증상이 시작되었고, 이후 상안정맥의 혈전이 생성되면서 증상이 점점 심해졌을 거라고 추측해볼 수 있다.
환자는 수술 이후 7일째 눈꺼풀과 결막의 부종, 복시가 사라지고, 경한 결막충혈만이 남았다. 경동맥정맥동루가 막히고 상안정맥의 혈전이 사라지면서 증상도 같이 완화된 것으로 보인다. 만약 환자에게 초진 시 안와연조직염만을 생각하여 항생제 치료에만 주력했다면, 치료가 더 늦어졌을 것이고 안과적 문제뿐만 아니라 혈전의 이동에 의한 생명을 위협하는 상황이 발생하였을 수도 있다. 본 증례에서는 좌안의 통증과 부종, 충혈, 안구운동장애, 복시를 보인 환자에서 초진 시 안와연조직염으로 생각하였으나 상안정맥혈전증과 경동맥해면정맥동루가 함께 진단되어 색전술과 스텐트 치료로 빠른 관해를 얻을 수 있었고, 상기 증상이 있을 때에는 다른 질환들과 감별하기 위하여 철저한 영상학적 검사가 필요할 것으로 생각된다.
Notes
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
References
Biography
나정호 / Jeong Ho Na
인제대학교 의과대학 해운대백병원 안과학교실
Department of Ophthalmology, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine