ņĢłĻ│╝ņŚÉņä£ ņ¦äļŗ© ļ░Å ņ╣śļŻī ļ¬®ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņé¼ņÜ®ļÉśļŖö ņĀÉņĢłņĀ£ļŖö ņäĖĻĘĀņä▒ ļ│æņøÉĻĘĀņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ┤ ņśżņŚ╝ļÉĀ ņłś ņ׳Ļ│Ā, ņØ┤ļŖö ļłłņØś Ļ░ÉņŚ╝ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØ┤ņ¢┤ņ¦ł ņłś ņ׳ļŗż[1]. ņĀÉņĢłņĀ£ļŖö ņ×¼ņé¼ņÜ® Ļ│╝ņĀĢņŚÉņä£ ļ»ĖņāØļ¼╝ņŚÉ ņśżņŚ╝ļÉĀ ņłśĻ░Ć ņ׳ņ£╝ļ®░ ņØ┤ņĀäņØś ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉ£ ņśżņŚ╝ļźĀņØĆ 0.07%ņŚÉņä£ 70%ļĪ£ ļŗżņ¢æĒĢśļŗż[2,3].
ņĀÉņĢłņĀ£ ņĢłņŚÉņä£ ņ×Éļ×Ć ļ»ĖņāØļ¼╝ņØĆ Ēö╝ļČĆ ņĀĢņāü ņāüņ×¼ĻĘĀņØ┤ ļ¦Äņ£╝ļéś staphylococcus aureusļéś ĻĘĖļ×ī ņØīņä▒ĻĘĀļÅä ļé«ņØĆ ļ╣äņ£©ļĪ£ ļ░£Ļ▓¼ļÉ£ļŗż[2]. ņśżņŚ╝ļÉ£ ņĢłņĢĮņØś ņé¼ņÜ®ņØ┤ ņŚ╝ņ”ØņØś ņøÉņØĖņØ┤ ļÉśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ ĒØöĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖĻ│Ā ņĀÉņĢłņĀ£ņŚÉ ļōżņ¢┤ņ׳ļŖö ļ│┤ņĪ┤ņĀ£Ļ░Ć Ļ│ĀņŚ¼ ņ׳ļŖö ņĢłņĢĮņŚÉņä£ ļ»ĖņāØļ¼╝ņØś ĒÖ£ņä▒ņØä ļ¦ēņĢäņŻ╝ļŖö ņŚŁĒĢĀņØä ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī, ņĢłņĢĮņŚÉņä£ ļ░░ņ¢æļÉ£ ņäĖĻĘĀņØ┤ Ļ░üļ¦ēņŚ╝, Ļ▓░ļ¦ēņŚ╝, ĻĘĖļ”¼Ļ│Ā ņĢłļé┤ņŚ╝ņØś ņøÉņØĖņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉ£ ņĀüņØ┤ ņ׳ļŗż[4].
ļīĆļČĆļČä ņØ┤ņĀäņØś ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ ļ░£Ēæ£ļÉ£ ņśżņŚ╝ļźĀĻ│╝ ĻĘĀ ļ░░ņ¢æĻ▓Ćņé¼ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļŖö ņé¼ņÜ®ļÉ£ ņĢłņĢĮņŚÉ ĻĄŁĒĢ£ļÉśņŚłļŗż[1-3]. ņØ┤ļ▓ł ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ļŖö ļŗżņ¢æĒĢ£ ņĢłņĢĮņØä ņé¼ņÜ®ņ×ÉņØś ņĀæņ┤ēņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ┤ ņØśļÅäņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņśżņŚ╝ņŗ£Ēé© Ēøä ņŚ░ņåŹ ļ░░ņ¢æ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļ│┤Ļ│Āņ×É ĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
ļīĆņāüĻ│╝ ļ░®ļ▓Ģ
ņØ┤ļ▓ł ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ ļ│┤ņĪ┤ņĀ£Ļ░Ć ĒżĒĢ©ļÉ£ ņĢłņĢĮĻ│╝ ĒżĒĢ©ļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņØĆ ņĢłņĢĮņØä ĒżĒĢ©ĒĢśņŚ¼ ĒĢŁņĢīļĀłļź┤ĻĖ░ņĀ£ 3ņóģļźś, ņØĖĻ│Ąļłłļ¼╝ 3ņóģļźś, ĒĢŁņāØņĀ£ 2ņóģļźś, ņŖżĒģīļĪ£ņØ┤ļō£ņĀ£Ļ░Ć 2ņóģļźśļĪ£ ņ┤Ø 10ņóģ 20Ļ░£ņØś ņĀÉņĢłņĀ£Ļ░Ć ĒżĒĢ©ļÉśņŚłļŗż(Table 1). Ļ░üĻ░ü ĒĢ£ ļ│æņØĆ ņāüņś©ņŚÉ, ĒĢ£ ļ│æņØĆ 2-5┬░CļĪ£ ļāēņןļ│┤Ļ┤ĆĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
ļ©╝ņĀĆ ņĢłņĢĮļ│æņØś ļÜ£Ļ╗æņØä ņŚ┤Ļ│Ā ņŗżĒŚśņ×ÉĻ░Ć ņØśļÅäņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│æņØś ņ×ģĻĄ¼ļź╝ ņåÉĻ░ĆļØĮņ£╝ļĪ£ ņśżņĀä 8ņŗ£ņÖĆ ņśżĒøä 8ņŗ£ ļæÉ ņ░©ļĪĆ ņśżņŚ╝ņŗ£ņ╝░ļŗż. ļ░░ņ¢æ Ļ│╝ņĀĢņŚÉņä£ ņĀÉņĢłĻĖ░ņØś ļüØņØ┤ ļ│æņØś ļÜ£Ļ╗æņŚÉ ļŗ┐ņ¦Ć ņĢŖļÅäļĪØ ņŻ╝ņØśĒĢśļ®░ ņĢłņĢĮ 1ļ░®ņÜĖņØä ņĀÉņĀüĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ░░ņ¢æĒĢśņśĆĻ│Ā, ņĢłņĢĮņØ┤ ņä£ļĪ£ ņżæļ│ĄļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖļÅäļĪØ ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņ▓½ ļ▓łņ¦Ė ĻĘĀ ļ░░ņ¢æĻ▓Ćņé¼ļŖö ņśżņŚ╝ņ£╝ļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ 2ņŻ╝ ļÆżņŚÉ ņŗ£Ē¢ēĒĢśņśĆļŗż. Ļ░üĻ░üņØś ņĢłņĢĮļ│æņŚÉņä£ ņ▒äņĘ©ĒĢ£ 1ļ░®ņÜĖņØĆ 5 mLņØś blood agar plates, Chocolate, MacConkey's ļ░░ņ¦ĆņŚÉņä£ ļ░░ņ¢æĒĢśņśĆĻ│Ā, ļ░░ņ¢æņØĆ ņŗżņś©Ļ│╝ ļé«ņØĆ ĻĖ░ņś©ņŚÉņä£ ļ¬©ļæÉ ņØ┤ļŻ©ņ¢┤ņĪīļŗż. ņäĖĻĘĀ ļ░░ņ¢æņØĆ Ēæ£ņżĆĒÖöļÉ£ ņŗżĒŚśņŗż ĻĖ░ņłĀņØä ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņØ┤ļŻ©ņ¢┤ņĪīļŗż. ļ░░ņ¢æņØĆ 2ņŻ╝ Ļ░äĻ▓®ņ£╝ļĪ£ 6ļ▓ł ņŗ£Ē¢ēļÉśņŚłļŗż. ņØ┤ĒøäņØś ļ░░ņ¢æļÅä ļÅÖņØ╝ĒĢ£ ļ░®ļ▓Ģņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņØ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļŖö ņŗżĒŚś ļģ╝ļ¼Ėņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ×äņāüņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņ£żļ”¼ņ£äņøÉĒÜīņØś ņŗ¼ņØś ļīĆņāüņØ┤ ņĢäļŗłļ»ĆļĪ£ ņŖ╣ņØĖņØä ņ¢╗ņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢśļŗż.
Ļ▓░ Ļ│╝
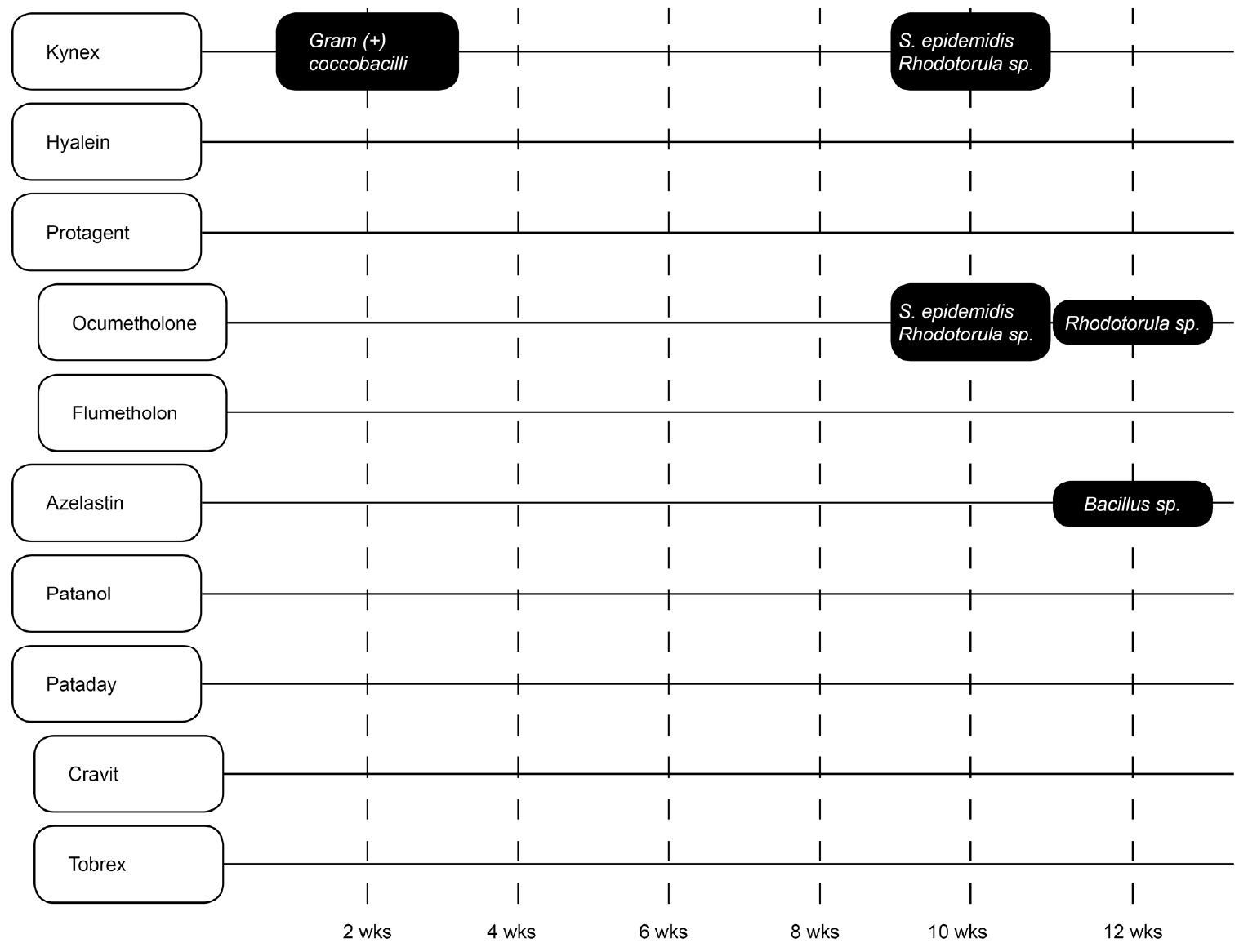
ļāēņןļ│┤Ļ┤ĆĻĄ░ņŚÉņä£ļŖö 3Ļ░£ņØś ņĢłņĢĮĻĄ░ņŚÉņä£ ņśżņŚ╝ņØ┤ ĒÖĢņØĖļÉśņŚłĻ│Ā(ļ│┤ņĪ┤ņĀ£Ļ░Ć ņŚåļŖö ņØĖĻ│Ąļłłļ¼╝, ņŖżĒģīļĪ£ņØ┤ļō£ņĀ£, ĒĢŁņĢīļĀłļź┤ĻĖ░ņĀ£), ņāüņś©ļ│┤Ļ┤ĆĻĄ░ņŚÉņä£ļŖö 4Ļ░£ņØś ņĢłņĢĮĻĄ░ņŚÉņä£ ņśżņŚ╝ņØ┤ ĒÖĢņØĖļÉśņŚłļŗż(ļ│┤ņĪ┤ņĀ£Ļ░Ć ņŚåļŖö ņØĖĻ│Ąļłłļ¼╝, ļ│┤ņĪ┤ņĀ£ļź╝ ĒżĒĢ©ĒĢ£ ņØĖĻ│Ąļłłļ¼╝, ņŖżĒģīļĪ£ņØ┤ļō£ņĀ£, ĒĢŁņĢīļĀłļź┤ĻĖ░ņĀ£) (Fig. 1, 2). ņ┤Ø 10ņóģņØś ņĢłņĢĮņØä ņŗżņś©Ļ│╝ ļāēņןļ│┤Ļ┤ĆņŚÉņä£ 6ĒÜīņö® ļ░░ņ¢æņØä ņŗżņŗ£ĒĢśļŹś ņżæ 13Ļ░£ņØś ņĢłņĢĮņØ┤ ņśżņŚ╝ļÉśņŚłņ£╝ļ®░ 5ņóģļźśņØś ļ»ĖņāØļ¼╝ņØ┤ Ļ▓ĆņČ£ļÉśņŚłļŗż(S. epidermidis, S. hominis, Rhodotorula spp., Corynebacterium spp. and Gram (+) bacilli). Ļ░Ćņן ĒØöĒĢ£ ņøÉņØĖĻĘĀņØĆ S.epidermidisļĪ£ 6Ļ░£ņØś ļ│æņŚÉņä£ Ļ▓ĆņČ£ļÉśņŚłļŗż(Table 1). ļŗżļźĖ ļ»ĖņāØļ¼╝ņØĆ 7ļ│æņŚÉņä£ ļ╣äņŖĘĒĢśĻ▓ī Ļ▓ĆņČ£ļÉśņŚłļŗż. ļāēņןļ│┤Ļ┤ĆĒĢśņŚÉņä£ 3Ļ░£ņØś ņĢłņĢĮ ņśżņŚ╝, 12ņŻ╝Ļ░ä 5ļ▓łņØś ĻĘĀ ļ░░ņ¢æĻ▓Ćņé¼ ņ¢æņä▒ņØä ļ│┤ņśĆņ£╝ļéś, ņāüņś©ļ│┤Ļ┤ĆņŚÉņä£ļŖö 4Ļ░£ņØś ņĢłņĢĮ ņśżņŚ╝ ļ░Å 8ļ▓łņØś ļ░░ņ¢æĻ▓Ćņé¼ ņ¢æņä▒ņØ┤ ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż.
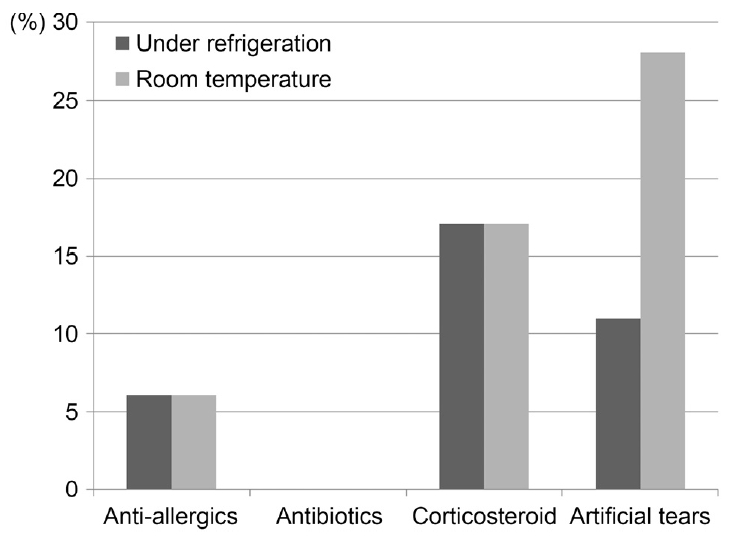
ļāēņןļ│┤Ļ┤Ć ļ░Å ņāüņś©ļ│┤Ļ┤ĆņŚÉņä£ ĒĢŁņĢīļĀłļź┤ĻĖ░ņĀ£ļŖö 6%ņŚÉņä£, ņŖżĒģīļĪ£ņØ┤ļō£ņĀ£ļŖö 17%ņØś ņ¢æņä▒ ļ░░ņ¢æļźĀņØä ļ│┤ņśĆļŗż. ļāēņןļ│┤Ļ┤ĆĒĢśņŚÉņä£ ņØĖĻ│Ąļłłļ¼╝ņØś ļ░░ņ¢æĻ▓Ćņé¼ ņ¢æņä▒ļźĀņØĆ 11%ņśĆņ£╝ļ®░, ņāüņś©ņŚÉņä£ļŖö 28%ņśĆļŗż(Fig. 3). ņ▓½ ļ▓łņ¦Ė ĻĘĀ ļ░░ņ¢æĻ▓Ćņé¼ņŚÉņä£ ņ¢æņä▒ņØ╝ ļĢī 2ņŻ╝ Ēøä ņŗ£Ē¢ēĒĢ£ Ļ▓Ćņé¼ņŚÉņä£ Ļ░ÖņØĆ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļ│┤ņØ┤ļŖö Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ļÅä ņ׳ņŚłņ£╝ļéś, ņ▓½ ļ▓łņ¦Ė Ļ▓Ćņé¼ņÖĆ ļæÉ ļ▓łņ¦Ė ļ░░ņ¢æĻ▓Ćņé¼ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝Ļ░Ć ņāüņØ┤ĒĢ£ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ļÅä ņ׳ņŚłļŗż.
Ļ│Ā ņ░░
ņĀÉņĢłņĀ£ļŖö ņāüņś©ļ│┤Ļ┤ĆĻ│╝ ļāēņןļ│┤Ļ┤Ć ļ¬©ļæÉņŚÉņä£ ņśżņŚ╝ņØ┤ ļÉĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ņØĖĻ│Ąļłłļ¼╝, ņŖżĒģīļĪ£ņØ┤ļō£ņĀ£, ĒĢŁņĢīļĀłļź┤ĻĖ░ņĀ£ ļ¬©ļæÉ ļæÉ Ļ░Ćņ¦Ć ņāüĒÖ®ņŚÉņä£ ņśżņŚ╝ņØ┤ ļÉĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ĒĢŁņāØņĀ£ ņĢłņĢĮņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņäĖĻĘĀ ļ░░ņ¢æņØ┤ Ļ┤Ćņ░░ļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢśņ£╝ļ®░ ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņÖĆ ļÅÖņØ╝ĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļ│┤ņŚ¼ ĒĢŁņāØņĀ£ļŖö ņäĖĻĘĀņśżņŚ╝ņ£╝ļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ ļ╣äĻĄÉņĀü ņĢłņĀäĒĢ£ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņāØĻ░üļÉ£ļŗż[5]. ĻĘĖļ¤¼ļéś Kim et al [6]ņØś ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ ĒĢŁņāØņĀ£ ņĢłņĢĮņŚÉņä£ ņ¦äĻĘĀ Ļ░ÉņŚ╝ņØ┤ ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśĻĖ░ļÅä ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ļ│┤ņĪ┤ņĀ£Ļ░Ć ņŚåļŖö ņØĖĻ│Ąļłłļ¼╝ņØĆ ņāüņś© ļ░Å ļāēņןļ│┤Ļ┤ĆņŚÉņä£ ĻĘĀ ļ░░ņ¢æĻ▓Ćņé¼ ņ¢æņä▒ņØ┤ ļ│┤ņśĆļŗż. ņØ┤ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļŖö ņŖżĒģīļĪ£ņØ┤ļō£ņĀ£(11%), ĒĢŁņāØņĀ£(5%), ļ▓ĀĒāĆņ░©ļŗ©ņĀ£(17%)ņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ ņØĖĻ│Ąļłłļ¼╝ņØś ņśżņŚ╝ ļ╣äņ£©(29%)ņØ┤ ļåÆļŗżļŖö ņØ┤ņĀäņØś Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ņÖĆ ņāüņØæĒĢ£ļŗż[1,3]. ĻĘĖļ¤¼ļéś ņĄ£Ļ│Ā ņśżņŚ╝ļźĀņØĆ ļ▓ĀĒāĆņ░©ļŗ©ņĀ£, ņŖżĒģīļĪ£ņØ┤ļō£ņĀ£, ņ£żĒÖ£ņĀ£ņŚÉņä£ ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗżļŖö ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÅä ņ׳ļŗż[7]. ļ│┤ņĪ┤ņĀ£Ļ░Ć ņŚåļŖö ņĢłņĢĮņŚÉņä£ ļé┤ņØĖņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒĢŁ ļ»ĖņāØļ¼╝ ĒÖ£ļÅÖņØ┤ ļéśĒāĆļé£ļŗżļŖö ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļÅä ņ׳ļŗż[1].
ņāüņś©ņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņ┤Ø 60ļ▓łņØś ļ░░ņ¢æ ņżæ 8Ļ░£, ļāēņןļ│┤Ļ┤ĆņŚÉņä£ļŖö 60ļ▓ł ņżæ 5Ļ░£ņØś ņĢłņĢĮņŚÉņä£(Ļ░üĻ░ü 13.3%ņÖĆ 8.3%) ĻĘĀ ļ░░ņ¢æĻ▓Ćņé¼ ņ¢æņä▒ņØä ļ│┤ņśĆļŗż. ļāēņןļ│┤Ļ┤ĆĒĢśņŚÉņä£ ņāüņś©ļ│┤Ļ┤ĆņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ ļŹö ļé«ņØĆ ņ¢æņä▒ļźĀņØä ļ│┤ņśĆĻ│Ā, ņØ┤ļŖö ļāēņןļ│┤Ļ┤ĆĒĢśņŚÉņä£ ļ»ĖņāØļ¼╝ņØś ļ│ĄņĀ£ņ£©ņØ┤ ļŹö ļé«ļŗżļŖö ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ņØś ļŗżļźĖ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØĆ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ņØ┤ļŗż[3]. ņØ┤ļ▓ł ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņśżņŚ╝ļÉ£ ņĢłņĢĮ ņżæņŚÉ 1ĒÜīņÜ® ņØĖĻ│ĄļłäņĢĪļ¦ī ņŗżņś©Ļ│╝ ļāēņןļ│┤Ļ┤ĆņŚÉņä£ ņ░©ņØ┤ļź╝ ļ│┤ņśĆņ£╝ļéś ĒĢŁņĢīļĀłļź┤ĻĖ░ņĀ£ņÖĆ ņŖżĒģīļĪ£ņØ┤ļō£ņĀ£ņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņ░©ņØ┤ļź╝ ļ│┤ņØ┤ņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢśļŗż. ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ņ░©ņØ┤ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ņä£ļŖö Ē¢źĒøä ļ│æņØś ņÜ®ĻĖ░, ļÜ£Ļ╗æņØś ļ░Ćļ┤ē ņŚ¼ļČĆ ļō▒ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼Ļ░Ć ĒĢäņÜöĒĢśĻ▓Āļŗż.
Staphylococcus spp., Bacillus spp., Proteus spp., Pseudomonas spp.ņØĆ ĻĄŁņåī ņĀÉņĢłņĀ£ņŚÉņä£ ĒØöĒ׳ ļ░£Ļ▓¼ļÉ£ļŗż[1,2,7,8]. ņØ┤ļ▓ł ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ ļ░░ņ¢æļÉ£ ļ»ĖņāØļ¼╝ ņżæ S. epidermidis, S. hominis, Rhodotorula spp., Corynebacterium spp., S. epidermidis, S. hominis, Rhodotorula spp.ņØĆ ĻĖ░ĒÜīĻ░ÉņŚ╝ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņāØĻ░üļÉśĻ│Ā, Corynebacterium spp.ņØ┤ ņĢł Ēæ£ļ®┤ņŚÉņä£ Ļ░Ćņן ĒØöĒĢśĻ▓ī ļ░£Ļ▓¼ļÉ£ ĻĘĀņØ┤ņŚłņ£╝ļ®░ ņĢłĻ│╝ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ļŖö ļ│æņøÉņä▒ņØ┤ ņŚåļŗżĻ│Ā Ļ░äņŻ╝ļÉ£ļŗż. ņĢ×ņŚÉņä£ ņ¢ĖĻĖēļÉ£ ĻĘĀļōżņØ┤ ĻĖ░ĒÜīĻ░ÉņŚ╝ĻĘĀņØ┤ĻĖ┤ ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī ņĀĢņāüņĢłņŚÉņä£ ņóģņóģ ņ¦æļØĮĒÖöļź╝ ņØ╝ņ£╝ĒéżĻĖ░ļÅä ĒĢ£ļŗż[9]. ņäĖĻĘĀņØś Ēżņ×ÉĻ░Ć ļ│┤ņĪ┤ņĀ£ņŚÉņä£ļÅä ņé┤ņĢäļé©ļŖö Ļ▓āņØä Ļ│ĀļĀżĒĢĀ ļĢī, ņØ┤ļĪĀņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ Bacillus spp.Ļ░Ć ļé©ņØĆ ņÜ®ņĢĪņŚÉņä£ Ļ░Ćņן ņÜ░ņäĖĒĢśļŗż[2]. ĒØźļ»ĖļĪ£ņÜ┤ Ļ▓āņØĆ Rhodotorula spp.ļŖö ļāēņןļ│┤Ļ┤ĆĒĢśņŚÉņä£ļ¦ī Ļ▓ĆņČ£ļÉśņŚłļŗż. Rhodotorula spp.ļŖö BasidiomycotaņØś ĒĢ£ ņóģļźśļĪ£ ļŗ©ņäĖĒż ĒÜ©ļ¬©ņØ┤ļŗż. ņ×ÉņŚ░ņŚÉ ĒØöĒ׳ ņĪ┤ņ×¼ĒĢśļŖö ņ£ĀĻĖ░ņ▓┤ņØ┤ļ®░, ļ®┤ņŚŁņØ┤ ņ¢ĄņĀ£ļÉ£ ĒÖśņ×ÉņŚÉņä£ļŖö Ļ░ÉņŚ╝ņØä ņØ╝ņ£╝Ēé¼ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż[10]. Rhodotorula spp.ņØś ņĀüņĀĢ ņä▒ņן ņś©ļÅäļŖö 20-30┬░CņØ┤ļéś, 4┬░CņØś ļé«ņØĆ ņś©ļÅäņŚÉņä£ļÅä ņāØņĪ┤ņØ┤ Ļ░ĆļŖźĒĢśļŗż[11]. ļ░śļ®┤ Corynebacterium spp.ļŖö 5┬░CņŚÉņä£ ņāØņĪ┤ĒĢĀ ņłś ņŚåņ¢┤ ļāēņןļ│┤Ļ┤ĆļÉ£ ņĢłņĢĮņŚÉņä£ņØś Ļ▓ĆņČ£ Ļ░ĆļŖźņä▒ņØĆ ļé«ļŗż[12].
ļ░░ņ¢æļÉ£ ļ»ĖņāØļ¼╝ņØĆ ļ░śļ│ĄļÉ£ ļ░░ņ¢æĻ▓Ćņé¼ņŚÉņä£ ļŗżņŗ£ ņ×ÉļØ╝ņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢśļŗż. 2ņŻ╝ ļÆżņŚÉ ņŗ£Ē¢ēļÉ£ ņ×¼ ļ░░ņ¢æĻ▓Ćņé¼ņŚÉņä£ ĻĘĀņØ┤ Ļ▓ĆņČ£ļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖĻ▒░ļéś ļČĆļČäņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ▓ĆņČ£ļÉśļŖö ļŹ░ļŖö ļ¬ć Ļ░Ćņ¦Ć ņØ┤ņ£ĀĻ░Ć ņ׳ņØä ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ņ▓½ ļ▓łņ¦ĖļĪ£ ĒÖśņ×ÉĻ░Ć ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśļŖö ļÅÖņĢł ņśżņŚ╝ņØä ļ¦ēĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ņÜ®ĻĖ░ņŚÉ ņ▓©Ļ░ĆļÉ£ ļ│┤ņĪ┤ņĀ£ņØś ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ ļĢīļ¼ĖņØ╝ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ļæÉ ļ▓łņ¦ĖļĪ£ ņśüņ¢æļČäņØś Ļ▓░ĒĢŹņØ┤ ļ»ĖņāØļ¼╝ņØś ņä▒ņןņØä ļ¦ēņĢäņżä ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ļ¦łņ¦Ćļ¦ēņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĀäņ▓┤ ņÜ®ĻĖ░ņØś ņśżņŚ╝ņØ┤ ņĢäļŗī ļ│æņØś ļüØ ļČĆļČäļ¦ī ņśżņŚ╝ļÉ£ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ņŚÉļŖö ņĢłņĢĮņØä ņĀÉņĢłĒĢśļŖö ļÅÖņĢł ļ»ĖņāØļ¼╝ņØ┤ ņö╗Ļ▓© ļéśĻ░ĆĻ▒░ļéś ņĀ£Ļ▒░ļÉĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ņØ┤ļ▓ł ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņØś ņĀ£ĒĢ£ņĀÉņ£╝ļĪ£ļŖö Ļ░ü ņĢłņĢĮņĀ£ņĀ£ņØś ņśżņŚ╝ņØ┤ ļÅÖņØ╝ĒĢśĻ▓ī ņØ┤ļŻ©ņ¢┤ņĪīļŖöņ¦ĆņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ĒĢ£Ļ│äĻ░Ć ņ׳ļŗż. ņØ┤ļź╝ ņĄ£ļīĆĒĢ£ ņżäņØ┤Ļ│Āņ×É ĒĢ£ ņŗżĒŚśņ×ÉĻ░Ć ļÅÖņØ╝ĒĢ£ ņŗ£Ļ░ä, ļÅÖņØ╝ĒĢ£ ļ░®ļ▓Ģņ£╝ļĪ£ ņŗżĒŚśņØä ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢśņśĆņ£╝ļéś ņāüĒÖ®ņŚÉ ļö░ļźĖ ņåÉņØś ņśżņŚ╝ļÅäļź╝ Ļ│ĀļĀżĒĢśļ®┤ ņ░©Ēøä ņŗżĒŚśņĀü ļ░®ļ▓Ģņ£╝ļĪ£ ĻĘĀņØś ļ░░ņ¢æ ņāüĒā£ļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśļŖö ņŚ░ĻĄ¼Ļ░Ć ĒĢäņÜöĒĢĀ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņāØĻ░üļÉ£ļŗż.
ņĢłņĢĮņØś ņśżņŚ╝ņØĆ ņĢłĻĄ¼ Ļ░ÉņŚ╝ņØä ņØ╝ņ£╝Ēé¼ ņłś ņ׳ĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ĒÖśņ×ÉļōżņŚÉĻ▓ī ņĢłņĢĮļ│æņØä ņĀüņĀłĒĢśĻ▓ī ļŗżļŻ©ļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ĻĄÉņ£ĪĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢ£ļŗż. ņØ┤ņĀäņØś ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ ņåÉĻ░ĆļØĮņØ┤ ņĢłņĢĮ ļ│æņŚÉ ļŗ┐ļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ ļ»ĖņāØļ¼╝ņØś ņśżņŚ╝ņØś ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ ņ£äĒŚśņØĖņ×ÉļĪ£ ļ░ØĒśĆņĪīļŗż[13]. ĒĢŁņāØņĀ£Ļ░Ć ĒżĒĢ©ļÉ£ ņĢłņĢĮņØĆ ļŗżļźĖ ņĢłņĢĮņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ ļé«ņØĆ ņśżņŚ╝ņØä ļ│┤ņØ┤ļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż.
ĒĢŁņāØņĀ£ļź╝ ņĀ£ņÖĖĒĢ£ ņĢłņĢĮņØĆ ņāüņś© ļ│┤Ļ┤Ć ļ░Å ļāēņןļ│┤Ļ┤ĆĒĢśņŚÉņä£ ņśżņŚ╝ļÉĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ĒŖ╣Ē׳ ļ│┤ņĪ┤ņĀ£Ļ░Ć ņŚåļŖö ņØĖĻ│Ąļłłļ¼╝ņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ņĢłņĢĮļ│æņØä ņ£äņāØņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļŗżļŻ©ļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ ņżæņÜöĒĢśļŗż. ĻĘĀ ļ░░ņ¢æĻ▓Ćņé¼ļŖö Ļ▓Ćņé¼ļź╝ ĒĢśļŖö ņŗ£ĻĖ░ņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝Ļ░Ć ļŗ¼ļØ╝ņ¦ł ņłś ņ׳ĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ņŚ░ņåŹ ļ░░ņ¢æĻ▓Ćņé¼ļź╝ ņŗ£Ē¢ēĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢśļŗż.





 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print






